CYR61: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''CYR61''' | == CYR61 (CCN1) == | ||
[[File:CCN1_Protein_Structure.svg|thumb|right|Diagram of the CCN1 protein structure]] | |||
'''CYR61''', also known as '''CCN1''', is a matricellular protein that plays a crucial role in cell signaling, development, and repair processes. It is a member of the [[CCN family]] of proteins, which are involved in various cellular functions including [[cell adhesion]], [[migration]], [[proliferation]], and [[differentiation]]. | |||
== Structure == | |||
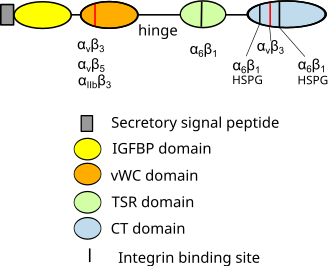
CYR61 is characterized by its modular structure, which includes several distinct domains that contribute to its diverse biological functions. The protein consists of the following domains: | |||
* An [[insulin-like growth factor binding protein]] (IGFBP) domain | |||
* A [[von Willebrand factor]] type C (vWC) domain | |||
* A thrombospondin type 1 (TSP1) repeat | |||
* A cysteine knot (CT) domain | |||
These domains allow CYR61 to interact with a variety of [[cell surface receptors]], [[extracellular matrix]] components, and [[growth factors]]. | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
CYR61 is involved in numerous physiological processes, including: | |||
* '''Angiogenesis''': CYR61 promotes the formation of new blood vessels by stimulating [[endothelial cell]] proliferation and migration. | |||
* '''Wound healing''': It plays a role in tissue repair by modulating the activity of [[fibroblasts]] and other cell types involved in the healing process. | |||
* '''Development''': CYR61 is essential for normal embryonic development, particularly in the formation of the [[cardiovascular system]] and [[skeletal system]]. | |||
== Clinical Significance == | == Clinical Significance == | ||
Alterations in CYR61 expression have been associated with various pathological conditions, including: | |||
* '''Cancer''': Overexpression of CYR61 has been observed in several types of [[cancer]], where it may contribute to tumor growth and metastasis. | |||
* '''Fibrosis''': Dysregulation of CYR61 is implicated in fibrotic diseases, where excessive tissue scarring occurs. | |||
* '''Inflammation''': CYR61 can modulate inflammatory responses, influencing the progression of inflammatory diseases. | |||
== | == Related Pages == | ||
* [[CCN family]] | |||
* [[Matricellular proteins]] | |||
* [[Cell signaling]] | |||
* [[Extracellular matrix]] | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Proteins]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Cell signaling]] | ||
[[Category:Developmental biology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 15 February 2025
CYR61 (CCN1)[edit]
CYR61, also known as CCN1, is a matricellular protein that plays a crucial role in cell signaling, development, and repair processes. It is a member of the CCN family of proteins, which are involved in various cellular functions including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and differentiation.
Structure[edit]
CYR61 is characterized by its modular structure, which includes several distinct domains that contribute to its diverse biological functions. The protein consists of the following domains:
- An insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP) domain
- A von Willebrand factor type C (vWC) domain
- A thrombospondin type 1 (TSP1) repeat
- A cysteine knot (CT) domain
These domains allow CYR61 to interact with a variety of cell surface receptors, extracellular matrix components, and growth factors.
Function[edit]
CYR61 is involved in numerous physiological processes, including:
- Angiogenesis: CYR61 promotes the formation of new blood vessels by stimulating endothelial cell proliferation and migration.
- Wound healing: It plays a role in tissue repair by modulating the activity of fibroblasts and other cell types involved in the healing process.
- Development: CYR61 is essential for normal embryonic development, particularly in the formation of the cardiovascular system and skeletal system.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Alterations in CYR61 expression have been associated with various pathological conditions, including:
- Cancer: Overexpression of CYR61 has been observed in several types of cancer, where it may contribute to tumor growth and metastasis.
- Fibrosis: Dysregulation of CYR61 is implicated in fibrotic diseases, where excessive tissue scarring occurs.
- Inflammation: CYR61 can modulate inflammatory responses, influencing the progression of inflammatory diseases.