Nifuroxazide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|An antibiotic used to treat diarrhea and colitis}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477002647 | |||
| image = Nifuroxazide.svg | |||
| image_size = 200px | |||
| image_alt = | |||
| image_caption = Chemical structure of Nifuroxazide | |||
}} | |||
'''Nifuroxazide''' is an [[antibiotic]] used primarily in the treatment of [[diarrhea]] and [[colitis]]. It is a nitrofuran derivative that acts by inhibiting bacterial [[enzyme]]s involved in the synthesis of [[nucleic acids]]. | |||
Nifuroxazide | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Nifuroxazide works by interfering with the [[bacterial]] [[enzyme|enzymatic]] processes necessary for the synthesis of [[nucleic acids]]. This action inhibits the growth and replication of [[bacteria]], making it effective against a broad spectrum of [[gram-positive]] and [[gram-negative]] bacteria. Unlike many other antibiotics, nifuroxazide is not absorbed into the bloodstream, which limits its action to the [[gastrointestinal tract]]. | |||
== | ==Uses== | ||
Nifuroxazide is primarily used to treat [[acute diarrhea]] caused by bacterial infections. It is also used in the management of [[colitis]] and other gastrointestinal infections. Due to its limited absorption, it is particularly useful in treating infections localized to the [[intestines]]. | |||
==Side Effects== | |||
Common side effects of nifuroxazide include [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], and [[abdominal pain]]. Since it is not absorbed systemically, it generally has fewer side effects compared to other antibiotics. However, allergic reactions such as [[rash]] and [[itching]] can occur. | |||
== | ==Contraindications== | ||
Nifuroxazide should not be used in individuals with known hypersensitivity to nitrofuran derivatives. It is also contraindicated in patients with [[glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency]] due to the risk of hemolytic anemia. | |||
==Administration== | |||
Nifuroxazide is available in oral formulations, including tablets and suspensions. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the patient's age and weight. | |||
== | |||
Nifuroxazide is | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Antibiotic]] | * [[Antibiotic]] | ||
* [[Diarrhea]] | * [[Diarrhea]] | ||
* [[Colitis]] | |||
* [[Nitrofuran]] | * [[Nitrofuran]] | ||
[[Category:Antibiotics]] | [[Category:Antibiotics]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal | [[Category:Nitrofurans]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal agents]] | |||
Revision as of 10:40, 15 February 2025
An antibiotic used to treat diarrhea and colitis
| Nifuroxazide | |
|---|---|
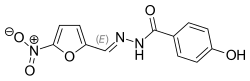
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Nifuroxazide is an antibiotic used primarily in the treatment of diarrhea and colitis. It is a nitrofuran derivative that acts by inhibiting bacterial enzymes involved in the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Mechanism of Action
Nifuroxazide works by interfering with the bacterial enzymatic processes necessary for the synthesis of nucleic acids. This action inhibits the growth and replication of bacteria, making it effective against a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Unlike many other antibiotics, nifuroxazide is not absorbed into the bloodstream, which limits its action to the gastrointestinal tract.
Uses
Nifuroxazide is primarily used to treat acute diarrhea caused by bacterial infections. It is also used in the management of colitis and other gastrointestinal infections. Due to its limited absorption, it is particularly useful in treating infections localized to the intestines.
Side Effects
Common side effects of nifuroxazide include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Since it is not absorbed systemically, it generally has fewer side effects compared to other antibiotics. However, allergic reactions such as rash and itching can occur.
Contraindications
Nifuroxazide should not be used in individuals with known hypersensitivity to nitrofuran derivatives. It is also contraindicated in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency due to the risk of hemolytic anemia.
Administration
Nifuroxazide is available in oral formulations, including tablets and suspensions. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the patient's age and weight.