Ozarelix: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A detailed overview of the drug Ozarelix}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| image = Ozarelix.svg | |||
| image_size = 250px | |||
| image_alt = Chemical structure of Ozarelix | |||
}} | |||
'''Ozarelix''' is a [[gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist]] (GnRH antagonist) that has been investigated for its potential use in the treatment of [[prostate cancer]] and [[benign prostatic hyperplasia]]. It works by inhibiting the secretion of [[luteinizing hormone]] (LH) and [[follicle-stimulating hormone]] (FSH), leading to a decrease in [[testosterone]] production. | |||
Ozarelix has been | |||
==Mechanism of Action== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Ozarelix functions by competitively binding to the | Ozarelix functions by competitively binding to the [[gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor]]s in the [[pituitary gland]]. This binding prevents the natural GnRH from stimulating the release of LH and FSH. The reduction in these hormones leads to decreased stimulation of the [[testes]] and a subsequent drop in testosterone levels, which is beneficial in conditions like prostate cancer where testosterone can promote tumor growth. | ||
==Clinical Applications== | |||
Ozarelix has been primarily studied for its role in managing prostate cancer. By lowering testosterone levels, it helps in reducing the size and growth rate of prostate tumors. Additionally, it has been explored for use in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia, a condition characterized by an enlarged prostate gland. | |||
==Pharmacokinetics== | ==Pharmacokinetics== | ||
The pharmacokinetic profile of Ozarelix | The pharmacokinetic profile of Ozarelix involves its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. It is typically administered via injection, allowing for direct entry into the bloodstream. The drug is designed to have a prolonged effect, reducing the frequency of administration required for therapeutic efficacy. | ||
The | |||
== | ==Side Effects== | ||
Ozarelix | Common side effects associated with Ozarelix include hot flashes, fatigue, and injection site reactions. As with other GnRH antagonists, there may be a risk of cardiovascular events, and monitoring is recommended during treatment. | ||
== | ==Research and Development== | ||
Ozarelix | Research into Ozarelix has included various clinical trials to assess its safety and efficacy. While promising results have been observed, further studies are needed to fully establish its role in clinical practice. | ||
[[ | ==Related pages== | ||
[[ | * [[Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist]] | ||
[[ | * [[Prostate cancer]] | ||
* [[Benign prostatic hyperplasia]] | |||
* [[Luteinizing hormone]] | |||
* [[Follicle-stimulating hormone]] | |||
[[Category:GnRH antagonists]] | |||
[[Category:Prostate cancer treatments]] | |||
Revision as of 04:05, 13 February 2025
A detailed overview of the drug Ozarelix
| Ozarelix | |
|---|---|
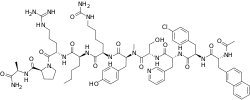
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Ozarelix is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist (GnRH antagonist) that has been investigated for its potential use in the treatment of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. It works by inhibiting the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), leading to a decrease in testosterone production.
Mechanism of Action
Ozarelix functions by competitively binding to the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors in the pituitary gland. This binding prevents the natural GnRH from stimulating the release of LH and FSH. The reduction in these hormones leads to decreased stimulation of the testes and a subsequent drop in testosterone levels, which is beneficial in conditions like prostate cancer where testosterone can promote tumor growth.
Clinical Applications
Ozarelix has been primarily studied for its role in managing prostate cancer. By lowering testosterone levels, it helps in reducing the size and growth rate of prostate tumors. Additionally, it has been explored for use in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia, a condition characterized by an enlarged prostate gland.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of Ozarelix involves its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. It is typically administered via injection, allowing for direct entry into the bloodstream. The drug is designed to have a prolonged effect, reducing the frequency of administration required for therapeutic efficacy.
Side Effects
Common side effects associated with Ozarelix include hot flashes, fatigue, and injection site reactions. As with other GnRH antagonists, there may be a risk of cardiovascular events, and monitoring is recommended during treatment.
Research and Development
Research into Ozarelix has included various clinical trials to assess its safety and efficacy. While promising results have been observed, further studies are needed to fully establish its role in clinical practice.