Verbal fluency test: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A test used to measure verbal fluency}} | |||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | |||
The '''verbal fluency test''' is a psychological assessment used to measure an individual's ability to produce words fluently. It is commonly used in neuropsychological evaluations to assess cognitive function, particularly in the domains of language and executive function. | |||
* | ==Overview== | ||
The verbal fluency test typically involves two main types of tasks: **phonemic fluency** and **semantic fluency**. In phonemic fluency tasks, individuals are asked to generate as many words as possible that begin with a specific letter, such as "F," "A," or "S," within a set time limit, usually one minute. In semantic fluency tasks, individuals are asked to produce words belonging to a specific category, such as "animals" or "fruits." | |||
==Purpose | ==Purpose== | ||
The | The test is used to evaluate the functioning of the frontal lobe and is sensitive to detecting cognitive impairments associated with various neurological conditions, including [[Alzheimer's disease]], [[Parkinson's disease]], and [[schizophrenia]]. It is also used in research to study language processing and executive control. | ||
==Procedure== | |||
During the test, participants are given a specific letter or category and instructed to say as many words as possible that fit the criteria within a limited time. The examiner records the number of words produced, as well as any repetitions or errors. The results are then compared to normative data to assess the individual's performance. | |||
==Scoring | ==Scoring== | ||
Scoring | Scoring is based on the number of correct words generated. Errors such as repetitions or words that do not fit the criteria are noted but do not count towards the total score. The results can provide insight into the individual's verbal abilities and cognitive flexibility. | ||
== | ==Applications== | ||
The verbal fluency test is widely used in clinical settings to assess cognitive function in patients with suspected neurological disorders. It is also used in research to explore the neural mechanisms underlying language and executive function. | |||
* | ==Related pages== | ||
* | * [[Cognitive test]] | ||
* | * [[Neuropsychological test]] | ||
* [[Executive functions]] | |||
== | ==References== | ||
* Lezak, M. D., Howieson, D. B., & Loring, D. W. (2004). ''Neuropsychological Assessment''. Oxford University Press. | |||
* Strauss, E., Sherman, E. M. S., & Spreen, O. (2006). ''A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms, and Commentary''. Oxford University Press. | |||
[[Category:Neuropsychological | [[Category:Neuropsychological tests]] | ||
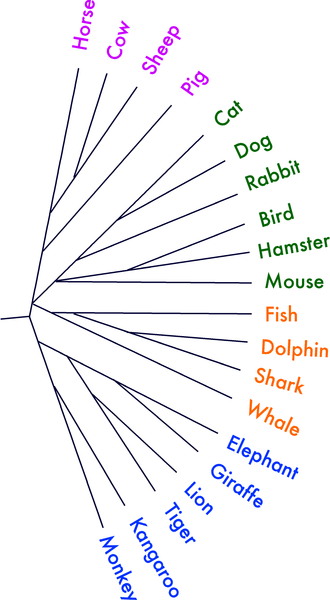
[[File:Animal addtree age7 nocat.png|thumb|right|An example of a semantic fluency task involving animals.]] | |||
Revision as of 15:45, 9 February 2025
A test used to measure verbal fluency
The verbal fluency test is a psychological assessment used to measure an individual's ability to produce words fluently. It is commonly used in neuropsychological evaluations to assess cognitive function, particularly in the domains of language and executive function.
Overview
The verbal fluency test typically involves two main types of tasks: **phonemic fluency** and **semantic fluency**. In phonemic fluency tasks, individuals are asked to generate as many words as possible that begin with a specific letter, such as "F," "A," or "S," within a set time limit, usually one minute. In semantic fluency tasks, individuals are asked to produce words belonging to a specific category, such as "animals" or "fruits."
Purpose
The test is used to evaluate the functioning of the frontal lobe and is sensitive to detecting cognitive impairments associated with various neurological conditions, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and schizophrenia. It is also used in research to study language processing and executive control.
Procedure
During the test, participants are given a specific letter or category and instructed to say as many words as possible that fit the criteria within a limited time. The examiner records the number of words produced, as well as any repetitions or errors. The results are then compared to normative data to assess the individual's performance.
Scoring
Scoring is based on the number of correct words generated. Errors such as repetitions or words that do not fit the criteria are noted but do not count towards the total score. The results can provide insight into the individual's verbal abilities and cognitive flexibility.
Applications
The verbal fluency test is widely used in clinical settings to assess cognitive function in patients with suspected neurological disorders. It is also used in research to explore the neural mechanisms underlying language and executive function.
Related pages
References
- Lezak, M. D., Howieson, D. B., & Loring, D. W. (2004). Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford University Press.
- Strauss, E., Sherman, E. M. S., & Spreen, O. (2006). A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms, and Commentary. Oxford University Press.