Trisodium citrate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Trisodium Citrate == | |||
[[File:Citric_acid_speciation.svg|thumb|right|Speciation of citric acid in solution.]] | |||
'''Trisodium citrate''' is the sodium salt of [[citric acid]] with the chemical formula Na_C_H_O_. It is sometimes referred to simply as "sodium citrate." It possesses a sour taste similar to that of citric acid and is commonly used as a food additive for its properties as a flavoring agent and preservative. | |||
== Chemical Properties == | |||
Trisodium citrate is a white, crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water. It is a weak acid and acts as a buffering agent, helping to maintain the pH of a solution. In aqueous solution, trisodium citrate dissociates into sodium ions and citrate ions, which can further interact with other ions in the solution. | |||
== | == Uses == | ||
Trisodium citrate is widely used in the food and beverage industry. It serves as an [[emulsifier]] in cheese production, helping to stabilize emulsions and prevent separation. It is also used in [[carbonated beverages]] to enhance flavor and as a preservative to extend shelf life. | |||
In the medical field, trisodium citrate is used as an [[anticoagulant]] in blood transfusions and as an alkalizing agent to treat metabolic acidosis. It is also found in some [[oral rehydration solutions]] to help restore electrolyte balance. | |||
[[Category: | == Production == | ||
[[Category: | Trisodium citrate is produced by neutralizing citric acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. The reaction results in the formation of sodium citrate and water. The product is then crystallized and dried to obtain the final powder form. | ||
== Safety and Handling == | |||
Trisodium citrate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. However, it should be handled with care to avoid inhalation or contact with eyes and skin, as it can cause irritation. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Citric acid]] | |||
* [[Sodium bicarbonate]] | |||
* [[Buffer solution]] | |||
== References == | |||
* "Sodium Citrate." PubChem, National Center for Biotechnology Information. Accessed October 2023. | |||
* "Trisodium Citrate." Food and Drug Administration. Accessed October 2023. | |||
[[Category:Food additives]] | |||
[[Category:Sodium compounds]] | |||
[[Category:Acid salts]] | |||
Revision as of 15:43, 9 February 2025
Trisodium Citrate
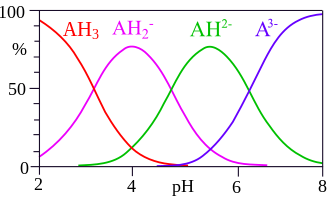
Trisodium citrate is the sodium salt of citric acid with the chemical formula Na_C_H_O_. It is sometimes referred to simply as "sodium citrate." It possesses a sour taste similar to that of citric acid and is commonly used as a food additive for its properties as a flavoring agent and preservative.
Chemical Properties
Trisodium citrate is a white, crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water. It is a weak acid and acts as a buffering agent, helping to maintain the pH of a solution. In aqueous solution, trisodium citrate dissociates into sodium ions and citrate ions, which can further interact with other ions in the solution.
Uses
Trisodium citrate is widely used in the food and beverage industry. It serves as an emulsifier in cheese production, helping to stabilize emulsions and prevent separation. It is also used in carbonated beverages to enhance flavor and as a preservative to extend shelf life.
In the medical field, trisodium citrate is used as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions and as an alkalizing agent to treat metabolic acidosis. It is also found in some oral rehydration solutions to help restore electrolyte balance.
Production
Trisodium citrate is produced by neutralizing citric acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. The reaction results in the formation of sodium citrate and water. The product is then crystallized and dried to obtain the final powder form.
Safety and Handling
Trisodium citrate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. However, it should be handled with care to avoid inhalation or contact with eyes and skin, as it can cause irritation.
Related Pages
References
- "Sodium Citrate." PubChem, National Center for Biotechnology Information. Accessed October 2023.
- "Trisodium Citrate." Food and Drug Administration. Accessed October 2023.