Dexamyl: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
[[Category:Barbiturates]] | [[Category:Barbiturates]] | ||
[[Category:Obsolete drugs]] | [[Category:Obsolete drugs]] | ||
<gallery caption="Dexamyl"> | |||
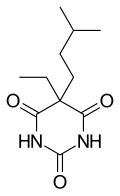
File:Amobarbital.svg|Amobarbital | |||
File:D-amphetamine.svg|D-amphetamine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:49, 20 February 2025
A combination drug used historically for weight loss and depression
Dexamyl was a pharmaceutical drug that combined two active ingredients: dextroamphetamine and amobarbital. It was primarily used in the mid-20th century for the treatment of depression and as an anorectic for weight loss. The drug was manufactured by the pharmaceutical company Smith, Kline & French and was available in tablet form.
Composition and Mechanism of Action[edit]
Dexamyl consisted of two main components:
- Dextroamphetamine: A central nervous system stimulant that increases the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. This action results in increased alertness, concentration, and energy levels, and it also suppresses appetite.
- Amobarbital: A barbiturate that acts as a sedative and hypnotic. It works by depressing the activity of the central nervous system, leading to relaxation and reduced anxiety.
The combination of these two drugs was intended to balance the stimulating effects of dextroamphetamine with the calming effects of amobarbital, providing a therapeutic effect for patients with depression and those needing appetite suppression.
Medical Uses[edit]
Dexamyl was prescribed for several conditions, including:
- Depression: The stimulant properties of dextroamphetamine were thought to help alleviate symptoms of depression by enhancing mood and energy levels.
- Weight Loss: As an anorectic, Dexamyl was used to suppress appetite in patients struggling with obesity.
- Anxiety and Tension: The sedative effects of amobarbital helped reduce anxiety and tension, making the drug useful for patients with these symptoms.
Side Effects and Risks[edit]
The use of Dexamyl was associated with several side effects, which included:
- Insomnia
- Nervousness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Nausea
- Addiction potential due to the presence of both a stimulant and a barbiturate.
The risk of addiction and the development of tolerance were significant concerns, leading to the eventual decline in the use of Dexamyl.
Historical Context and Discontinuation[edit]
Dexamyl was widely used during the 1950s and 1960s. However, as the understanding of drug dependence and the risks associated with barbiturates and amphetamines grew, the medical community began to move away from such combination drugs. The development of newer antidepressants and appetite suppressants with better safety profiles also contributed to the decline in Dexamyl's popularity.
By the late 1970s, Dexamyl was largely phased out of use, and it is no longer available on the market today.
Related Pages[edit]
- Dexamyl
-
Amobarbital
-
D-amphetamine