Decynium-22: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Category:Neuroscience]] | [[Category:Neuroscience]] | ||
[[Category:Pharmacology]] | [[Category:Pharmacology]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Pseudoisocyanine.svg|Pseudoisocyanine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:07, 25 February 2025
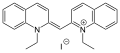
Decynium-22 is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of pseudoisocyanine dyes. It is primarily used in scientific research as a tool to study various biological processes, particularly those involving neurotransmitter transporters.
Chemical Properties[edit]
Decynium-22 is characterized by its pseudoisocyanine structure, which contributes to its unique chemical properties. The compound is known for its ability to interact with certain types of membrane transport proteins, making it a valuable probe in neuroscience and pharmacology.
Biological Applications[edit]
In biological research, Decynium-22 is often used to inhibit the function of specific neurotransmitter transporters. This inhibition allows researchers to study the role of these transporters in synaptic transmission and neurotransmitter reuptake. The compound has been particularly useful in studies involving the serotonin transporter and the norepinephrine transporter.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Decynium-22 functions by binding to the transporter proteins, thereby blocking the reuptake of neurotransmitters into the presynaptic neuron. This action results in increased levels of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft, which can be measured to assess the activity of the transporters.
Research Implications[edit]
The use of Decynium-22 in research has provided significant insights into the mechanisms of neurotransmitter regulation and the potential for targeting these transporters in the treatment of various neurological disorders. Its ability to selectively inhibit transporter activity makes it a powerful tool in the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Related Pages[edit]
-
Pseudoisocyanine