2-MDP: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
[[Category:Analgesics]] | [[Category:Analgesics]] | ||
[[Category:Chemical compounds]] | [[Category:Chemical compounds]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:2-MDP.svg|2-MDP | |||
File:U-23,807A_synthesis.svg|U-23,807A synthesis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:09, 17 February 2025
2-MDP[edit]

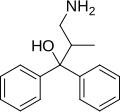
2-MDP (2-methyl-3,3-diphenyl-3-propanol) is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of opioid analgesics. It is known for its potential use in pain management due to its interaction with the opioid receptors in the central nervous system.
Chemical Structure[edit]
2-MDP is characterized by its unique chemical structure, which includes a methyl group attached to a diphenylpropanol backbone. This structure is crucial for its activity as an opioid agonist.
Pharmacology[edit]
2-MDP acts primarily as an agonist at the mu-opioid receptor, which is responsible for its analgesic effects. The interaction with these receptors leads to the inhibition of neurotransmitter release, resulting in decreased perception of pain.
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis of 2-MDP involves several chemical reactions, starting from basic organic compounds. The process typically includes the formation of the diphenylpropanol core, followed by the introduction of the methyl group.

Clinical Use[edit]
While 2-MDP has shown potential in preclinical studies, its clinical use is limited. Research is ongoing to determine its efficacy and safety profile compared to other opioid analgesics.
Side Effects[edit]
As with other opioids, 2-MDP may cause side effects such as nausea, constipation, drowsiness, and the potential for addiction. These effects are due to its action on the central nervous system and the body's natural opioid receptors.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of 2-MDP varies by country. In many regions, it is classified as a controlled substance due to its potential for abuse and addiction.
Related Compounds[edit]
2-MDP is related to other opioid compounds such as morphine, codeine, and synthetic opioids like fentanyl. These compounds share similar mechanisms of action but differ in potency, duration of action, and side effect profiles.
Related Pages[edit]
-
2-MDP
-
U-23,807A synthesis