Turgor pressure: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
[[Category:Plant physiology]] | [[Category:Plant physiology]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Turgor_pressure_on_plant_cells_diagram.svg|Diagram showing turgor pressure on plant cells | |||
File:Turgid.svg|Illustration of a turgid plant cell | |||
File:Mature_squirting_cucumber.jpg|Mature squirting cucumber | |||
File:Tree_growing_out_of_rock_in_Coire_Earb_-_geograph.org.uk_-_853941.jpg|Tree growing out of rock | |||
File:Stomata_opened_and_closed_unlabelled.svg|Stomata opened and closed | |||
File:Sismonastia_de_la_Mimosa_pudica.jpg|Sismonastia of the Mimosa pudica | |||
File:Shaggy_Ink_Caps_busting_through_asphalt.jpg|Shaggy Ink Caps busting through asphalt | |||
File:Pressurebomb.svg|Diagram of a pressure bomb | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:04, 18 February 2025
Turgor Pressure[edit]

Turgor pressure is the pressure exerted by the fluid (usually water) inside the cell against the cell wall. It is a critical factor in maintaining the structural integrity and rigidity of plant cells, allowing them to remain turgid and upright. Turgor pressure is essential for various physiological processes in plants, including growth, nutrient transport, and the opening and closing of stomata.
Mechanism[edit]
Turgor pressure is generated when water enters the plant cell by osmosis, causing the vacuole to swell. The cell wall, being rigid, resists this expansion, creating pressure within the cell. This pressure is balanced by the osmotic pressure of the cell's contents, maintaining the cell's shape and firmness.

Importance in Plants[edit]
Turgor pressure plays a vital role in maintaining the plant's structure. It helps keep the plant upright and supports the leaves and flowers. When turgor pressure is lost, plants wilt and droop, as seen in conditions of water scarcity.
Growth and Movement[edit]
Turgor pressure is also involved in plant growth and movement. It drives cell expansion, which is crucial for plant growth. Additionally, it is involved in rapid movements such as the closing of Mimosa pudica leaves and the explosive dispersal of seeds in plants like the squirting cucumber.

Environmental Adaptations[edit]
Plants have adapted to various environments by modifying their turgor pressure. For example, some plants can grow in rocky environments by exerting pressure to break through hard surfaces.

Stomatal Function[edit]
Turgor pressure is crucial in the opening and closing of stomata, which are small openings on the leaf surface that regulate gas exchange and water loss. Changes in turgor pressure in the guard cells surrounding each stoma control its aperture.

Applications[edit]
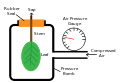
Turgor pressure is measured using a device called a pressure bomb or pressure chamber, which helps in understanding plant water status and irrigation needs.

Related Pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Diagram showing turgor pressure on plant cells
-
Illustration of a turgid plant cell
-
Mature squirting cucumber
-
Tree growing out of rock
-
Stomata opened and closed
-
Sismonastia of the Mimosa pudica
-
Shaggy Ink Caps busting through asphalt
-
Diagram of a pressure bomb