Emtricitabine/tenofovir: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
[[Category:HIV/AIDS prevention]] | [[Category:HIV/AIDS prevention]] | ||
[[Category:Combination drugs]] | [[Category:Combination drugs]] | ||
== Emtricitabine/tenofovir == | |||
<gallery> | |||
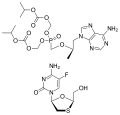
File:Tenofovir disoproxil and emtricitabine.svg|Emtricitabine/tenofovir chemical structure | |||
File:Truvada.JPG|Truvada tablets | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:25, 20 February 2025
Combination antiretroviral medication
| Emtricitabine/tenofovir | |
|---|---|

| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Emtricitabine/tenofovir is a combination antiretroviral medication used in the treatment and prevention of HIV/AIDS. It is a fixed-dose combination of two antiretroviral drugs: emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil. This combination is commonly marketed under the brand name Truvada, among others.
Medical uses
Emtricitabine/tenofovir is primarily used in the treatment of HIV infection in combination with other antiretroviral agents. It is also used as a part of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV in high-risk populations.
Treatment of HIV
In the treatment of HIV, emtricitabine/tenofovir is used as part of a highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) regimen. It works by inhibiting the action of reverse transcriptase, an enzyme crucial for the replication of HIV.
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
For PrEP, emtricitabine/tenofovir is taken by HIV-negative individuals to prevent infection. Clinical trials have shown that when taken consistently, it significantly reduces the risk of HIV transmission.
Mechanism of action
Emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil are both reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Emtricitabine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), while tenofovir disoproxil is a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NtRTI). They work by blocking reverse transcriptase, an enzyme that HIV needs to replicate its genetic material and multiply.
Side effects
Common side effects of emtricitabine/tenofovir include nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, and fatigue. Long-term use may lead to kidney problems and bone density loss. Regular monitoring of kidney function and bone health is recommended for patients on this medication.
History
Emtricitabine/tenofovir was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2004 for the treatment of HIV. In 2012, it was approved for use as PrEP, marking a significant advancement in HIV prevention strategies.
Also see
References
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
Emtricitabine/tenofovir
-
Emtricitabine/tenofovir chemical structure
-
Truvada tablets