Diabetic retinopathy: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Diabetic retinopathy | |||
| image = [[File:Fundus_-_diabetic_retinopathy.png|left|thumb|Fundus photograph showing diabetic retinopathy]] | |||
| caption = Fundus photograph showing diabetic retinopathy | |||
| field = [[Ophthalmology]] | |||
| synonyms = | |||
| symptoms = [[Floaters]], [[blurry vision]], [[dark areas of vision]], [[difficulty perceiving colors]] | |||
| complications = [[Blindness]], [[retinal detachment]] | |||
| onset = Gradual | |||
| duration = Long term | |||
| types = [[Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy]], [[proliferative diabetic retinopathy]] | |||
| causes = [[Diabetes mellitus]] | |||
| risks = Poor [[blood sugar control]], [[hypertension]], [[high cholesterol]], [[smoking]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Eye examination]], [[fundus photography]], [[optical coherence tomography]] | |||
| differential = [[Hypertensive retinopathy]], [[retinal vein occlusion]] | |||
| prevention = [[Blood sugar control]], [[blood pressure control]], regular [[eye exams]] | |||
| treatment = [[Laser photocoagulation]], [[anti-VEGF therapy]], [[vitrectomy]] | |||
| medication = [[Anti-VEGF drugs]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, can lead to [[vision loss]] if untreated | |||
| frequency = Common in people with [[diabetes]] | |||
}} | |||
'''Diabetic retinopathy''' is a [[diabetes]]-related eye condition that affects the [[retina]]. It is a serious sight-threatening complication of diabetes. | '''Diabetic retinopathy''' is a [[diabetes]]-related eye condition that affects the [[retina]]. It is a serious sight-threatening complication of diabetes. | ||
[[File:Diabetic retinopathy-NIE.gif|left|thumb|Diabetic retinopathy NIE]] | |||
[[File:Diabetic retinopathy-NIE.gif|thumb|Diabetic retinopathy NIE]] | == Introduction == | ||
== | |||
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high [[blood sugar]] levels. Over time, these high levels can cause damage to various parts of the body, including the retina, which is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. This damage is known as diabetic retinopathy. | Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high [[blood sugar]] levels. Over time, these high levels can cause damage to various parts of the body, including the retina, which is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. This damage is known as diabetic retinopathy. | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| Line 16: | Line 35: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems. However, as the condition progresses, it can lead to blindness. Symptoms can include: | In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems. However, as the condition progresses, it can lead to blindness. Symptoms can include: | ||
| Line 25: | Line 43: | ||
* Spots or dark strings floating in your vision ([[floaters]]) | * Spots or dark strings floating in your vision ([[floaters]]) | ||
* Vision loss | * Vision loss | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can occur as a result of high blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and tobacco use. | Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can occur as a result of high blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and tobacco use. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the stage of the disease and the specific problems that need to be addressed. Options may include: | Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the stage of the disease and the specific problems that need to be addressed. Options may include: | ||
| Line 34: | Line 50: | ||
* Injection of medication into the eye | * Injection of medication into the eye | ||
* Surgery | * Surgery | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
The best way to prevent diabetic retinopathy is to manage your diabetes well. This includes: | The best way to prevent diabetic retinopathy is to manage your diabetes well. This includes: | ||
| Line 41: | Line 56: | ||
* Controlling your cholesterol levels | * Controlling your cholesterol levels | ||
* Quitting smoking | * Quitting smoking | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Diabetes]] | * [[Diabetes]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 62: | ||
* [[Blood pressure]] | * [[Blood pressure]] | ||
* [[Cholesterol]] | * [[Cholesterol]] | ||
[[Category:Diabetes]] | [[Category:Diabetes]] | ||
[[Category:Eye diseases]] | [[Category:Eye diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Endocrinology]] | [[Category:Endocrinology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:42, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Diabetic retinopathy | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Floaters, blurry vision, dark areas of vision, difficulty perceiving colors |
| Complications | Blindness, retinal detachment |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, proliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| Causes | Diabetes mellitus |
| Risks | Poor blood sugar control, hypertension, high cholesterol, smoking |
| Diagnosis | Eye examination, fundus photography, optical coherence tomography |
| Differential diagnosis | Hypertensive retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion |
| Prevention | Blood sugar control, blood pressure control, regular eye exams |
| Treatment | Laser photocoagulation, anti-VEGF therapy, vitrectomy |
| Medication | Anti-VEGF drugs |
| Prognosis | Variable, can lead to vision loss if untreated |
| Frequency | Common in people with diabetes |
| Deaths | N/A |
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes-related eye condition that affects the retina. It is a serious sight-threatening complication of diabetes.
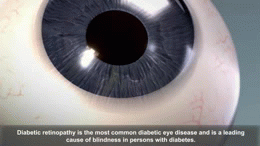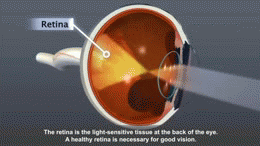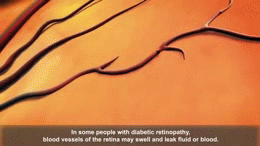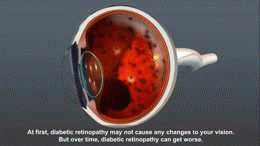
Introduction[edit]
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood sugar levels. Over time, these high levels can cause damage to various parts of the body, including the retina, which is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. This damage is known as diabetic retinopathy.
Symptoms[edit]
In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems. However, as the condition progresses, it can lead to blindness. Symptoms can include:
- Blurred vision
- Fluctuating vision
- Dark or empty areas in your vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Spots or dark strings floating in your vision (floaters)
- Vision loss
Causes[edit]
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can occur as a result of high blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and tobacco use.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the stage of the disease and the specific problems that need to be addressed. Options may include:
- Laser treatment
- Injection of medication into the eye
- Surgery
Prevention[edit]
The best way to prevent diabetic retinopathy is to manage your diabetes well. This includes:
- Controlling your blood sugar levels
- Controlling your blood pressure
- Controlling your cholesterol levels
- Quitting smoking


