Diphenyl oxalate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category:Organic compounds]] | [[Category:Organic compounds]] | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
== Diphenyl_oxalate == | |||
<gallery> | |||
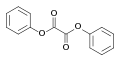
File:Diphenyl_oxalate.svg|Structural formula of Diphenyl oxalate | |||
File:Diphenyl_oxalate_3D_ball.png|3D ball model of Diphenyl oxalate | |||
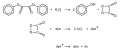
File:Cyalume-reactions.svg|Chemical reactions involving Diphenyl oxalate | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:07, 18 February 2025
Diphenyl oxalate (C14H10O4) is a chemical compound that plays a significant role in the field of chemistry, particularly in the production of chemiluminescence. This compound, when mixed with a suitable fluorophore and hydrogen peroxide, undergoes a chemical reaction that results in the emission of light without the need for an external light source. This process is utilized in various applications, including glow sticks, bioluminescence research, and certain analytical methods in biochemistry and medical diagnostics.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
Diphenyl oxalate consists of two phenyl groups attached to an oxalate group. The oxalate group is a dicarboxylate with the formula C2O4, which acts as a strong electron-withdrawing group, facilitating the chemiluminescent reaction. This compound is typically solid at room temperature and requires careful handling due to its reactive nature.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
The chemiluminescent reaction involving diphenyl oxalate is initiated by the decomposition of the compound in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. This reaction produces an unstable intermediate, which then transfers energy to a dye (fluorophore), resulting in the emission of light. The color of the light depends on the specific fluorophore used in the reaction.
Applications[edit]
Diphenyl oxalate finds its applications primarily in the creation of glow sticks, where it is encapsulated along with a fluorophore in a plastic tube. Upon bending the tube, the inner glass vial containing hydrogen peroxide breaks, mixing with the diphenyl oxalate and the dye, thus initiating the light-emitting reaction. Beyond entertainment, this reaction has practical applications in safety equipment, military operations, and as markers in search and rescue operations.
In scientific research, diphenyl oxalate is used in bioluminescence studies to understand the mechanisms of light production in biological organisms. It also serves as a tool in biochemistry and medical diagnostics, where its light-emitting property is utilized in assays and tests that require the detection of specific biological molecules.
Safety and Handling[edit]
While diphenyl oxalate is not considered highly toxic, it should be handled with care in a well-ventilated area, wearing appropriate protective equipment. Direct contact with the skin or eyes should be avoided, and spills should be cleaned promptly to prevent accidental exposure.
Environmental Impact[edit]
The environmental impact of diphenyl oxalate is minimal when used and disposed of properly. However, as with all chemicals, responsible use and disposal practices should be followed to minimize any potential harm to the environment.
See Also[edit]
Diphenyl_oxalate[edit]
-
Structural formula of Diphenyl oxalate
-
3D ball model of Diphenyl oxalate
-
Chemical reactions involving Diphenyl oxalate