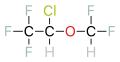Halogenated ether: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Halogenated ether gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Isoflurane skeletal formula.svg|Isoflurane skeletal formula | |||
File:Simpson James Young signature picture.jpg|Simpson James Young signature picture | |||
File:Hexafluoropropylene oxide.png|Hexafluoropropylene oxide | |||
File:Decabromodiphenyl ether.svg|Decabromodiphenyl ether | |||
File:HD TBBPA-DBPE (1).png|HD TBBPA-DBPE | |||
File:Sevoflurane.png|Sevoflurane | |||
File:Isoflurane structure.png|Isoflurane structure | |||
File:Desflurane.png|Desflurane | |||
File:Methoxyflurane.png|Methoxyflurane | |||
File:Enflurane.png|Enflurane | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:20, 3 March 2025
Halogenated ether refers to a group of chemical compounds that consist of an ether in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by halogen atoms. These compounds are significant in various fields, including medicine, chemistry, and industry, due to their unique properties and applications. The most notable use of halogenated ethers is in anesthesia, where they serve as potent inhalational anesthetics.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
Halogenated ethers are characterized by their chemical structure, which includes an ether group (an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups) and one or more halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) replacing hydrogen atoms in the molecule. This substitution significantly alters the physical and chemical properties of the ether, including its boiling point, solubility, and reactivity.
The presence of halogen atoms makes these compounds highly effective as solvents and anesthetics. Their volatility and ability to induce reversible loss of consciousness with minimal side effects have made them invaluable in the field of surgery and dentistry.
Medical Applications[edit]
In the medical field, halogenated ethers are primarily used as inhalational anesthetics. The most commonly used compounds in this category include:
- Sevoflurane: Known for its rapid onset and recovery times, making it ideal for outpatient surgeries. - Isoflurane: Valued for its potency and muscle-relaxing properties. - Desflurane: Characterized by its very rapid onset and recovery, although it can irritate the airways.
These agents work by depressing the central nervous system, leading to a reversible state of unconsciousness and analgesia. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood but is believed to involve interactions with various neurotransmitter systems in the brain.
Safety and Environmental Concerns[edit]
While halogenated ethers are invaluable in medicine, they also pose potential risks and environmental concerns. Prolonged exposure or high concentrations can lead to health issues for medical staff, including liver and kidney damage, reproductive effects, and central nervous system disorders. Furthermore, some halogenated ethers have been identified as potent greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change.
Regulation and Handling[edit]
Due to their potential health and environmental impacts, the use and disposal of halogenated ethers are regulated under various international and national guidelines. Healthcare facilities are required to implement strict handling and waste management protocols to minimize occupational exposure and environmental release.
Conclusion[edit]
Halogenated ethers play a critical role in modern medicine, particularly in the field of anesthesia. Their unique chemical properties allow for safe and effective induction of anesthesia, contributing significantly to the advancement of surgical procedures. However, their use must be carefully managed to mitigate potential health and environmental risks.
Halogenated ether gallery[edit]
-
Isoflurane skeletal formula
-
Simpson James Young signature picture
-
Hexafluoropropylene oxide
-
Decabromodiphenyl ether
-
HD TBBPA-DBPE
-
Sevoflurane
-
Isoflurane structure
-
Desflurane
-
Methoxyflurane
-
Enflurane