Electronic prescribing: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
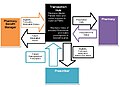
File:Electronic_Prescribing,_How_it_works.jpeg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:03, 16 February 2025
Electronic prescribing (e-prescribing or eRx) is the computer-based electronic generation, transmission, and filling of a medical prescription, taking the place of paper and faxed prescriptions. E-prescribing allows a physician, pharmacist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant to electronically transmit a new prescription or renewal authorization to a community or mail-order pharmacy. It is a significant aspect of the digital health landscape, aiming to improve the efficiency of the prescription process and reduce errors associated with traditional prescription scripts.
Overview[edit]
E-prescribing is part of a larger movement towards electronic medical records (EMR) and health information exchange (HIE), which seeks to digitize health and medical records to improve the efficiency and quality of healthcare. E-prescribing systems can be integrated with existing clinical information systems to allow healthcare providers to send prescriptions to pharmacies electronically, check for drug interactions, and view patients' medication histories.
Benefits[edit]
The benefits of e-prescribing are manifold. It reduces the likelihood of prescription errors caused by illegible handwriting and misunderstood oral prescriptions. It also streamlines the prescribing process, saving time for both healthcare providers and patients. By checking for drug interactions and allergies, e-prescribing can enhance patient safety. Additionally, it facilitates prescription management and refill processes, making it easier for patients to obtain their medications.
Challenges[edit]
Despite its benefits, e-prescribing faces several challenges. These include issues related to software interoperability, the cost of implementing e-prescribing systems, and the need for adequate training for healthcare providers. Privacy and security concerns also arise, as with any digital health information system, necessitating robust data protection measures.
Regulations and Standards[edit]
In many countries, e-prescribing is subject to specific regulations and standards aimed at ensuring the security and privacy of patient information. In the United States, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient data. Additionally, the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003 has provisions that encourage the use of e-prescribing in the Medicare program.
Implementation[edit]
Implementing e-prescribing involves several steps, including selecting an e-prescribing system, integrating it with existing clinical systems, training staff, and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and standards. Successful implementation requires collaboration among healthcare providers, IT professionals, and system vendors.
Future Directions[edit]
The future of e-prescribing includes advancements in technology that will further integrate e-prescribing systems with broader health information technologies. This integration will likely enhance the functionality of e-prescribing, such as improved decision support systems for medication management and better interoperability with other digital health platforms.
See Also[edit]