Dopamine receptor D5: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{GPCR-stub}} | {{GPCR-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
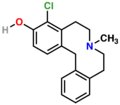
File:4-Chloro-7-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,14-hexahydrodibenz-d,g-azecin-3-ol.png|4-Chloro-7-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,14-hexahydrodibenz-d,g-azecin-3-ol | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:04, 17 February 2025
Dopamine receptor D5, also known as DRD5, is a type of dopamine receptor that has a significant role in the human body. It is one of the five subtypes of dopamine receptors and is primarily found in the brain and kidney.
Structure[edit]
The DRD5 receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor that is located on the cell surface. It is composed of seven transmembrane domains, which are characteristic of this type of receptor. The structure of the DRD5 receptor allows it to interact with dopamine, a type of neurotransmitter, and transmit signals within the cell.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the DRD5 receptor is to bind to dopamine and initiate a series of reactions within the cell. This process is known as signal transduction. The activation of the DRD5 receptor by dopamine leads to an increase in the production of cyclic AMP, a molecule that plays a crucial role in many biological processes.
In the brain, the DRD5 receptor is involved in the regulation of memory and learning. It is also thought to play a role in the development of certain neurological disorders, such as schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease.
In the kidney, the DRD5 receptor helps to regulate blood pressure by controlling the balance of salt and water in the body.
Clinical significance[edit]
Due to its role in the brain and kidney, the DRD5 receptor is a potential target for the treatment of several medical conditions. Drugs that can modulate the activity of the DRD5 receptor may be useful in the treatment of neurological disorders, such as schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease, as well as conditions related to blood pressure regulation.
See also[edit]
- Dopamine receptor
- Dopamine receptor D1
- Dopamine receptor D2
- Dopamine receptor D3
- Dopamine receptor D4
References[edit]
<references />
This GPCR-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
4-Chloro-7-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,14-hexahydrodibenz-d,g-azecin-3-ol