GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{neuroscience-stub}} | {{neuroscience-stub}} | ||
{{psychopharmacology-stub}} | {{psychopharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gamma-Aminobuttersäure_-_gamma-aminobutyric_acid.svg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
File:GABAA-receptor-protein-example-en.svg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
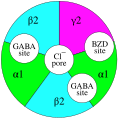
File:GABAA_receptor_binding_sites.jpg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
File:GABA_synapse.jpg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
File:Original_synthesis_of_Barbituric_acid.jpg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
File:Current_synthesis_of_barbituric_acid.jpg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
File:Synthesis_and_discovery_of_chlordiazepoxide.jpg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
File:BarbituratesR_groups.jpg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
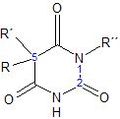
File:1,4-Benzodiazepin-2-on.png|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
File:Neurosteroid_R-group_analogs.jpg|GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:09, 18 February 2025
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
The GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator is a type of pharmacological agent that enhances the activity of the GABAA receptor, a type of protein that responds to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These modulators do not bind to the same part of the receptor as GABA itself, but instead bind to distinct sites on the protein.
Mechanism of Action
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators increase the effect of GABA at the GABAA receptor by increasing the frequency of chloride channel opening events, which leads to an increase in the flow of chloride ions into the neuron. This results in a hyperpolarization of the neuron and a decrease in neuronal excitability.
Therapeutic Use
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators have a wide range of therapeutic uses. They are used in the treatment of conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and epilepsy. Some of the most commonly used drugs in this class include benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and alcohol.
Side Effects
While GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators can be effective in treating a variety of conditions, they also have potential side effects. These can include drowsiness, confusion, and dependency. Long-term use can lead to tolerance and withdrawal symptoms.
Research
Research into GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators is ongoing, with scientists seeking to develop new drugs that can modulate the GABAA receptor with fewer side effects and less potential for dependency.

This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
This article is a Psychopharmacology-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
-
GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator