Pleural empyema: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Thoracic surgical procedures]] | [[Category:Thoracic surgical procedures]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
== Pleural empyema == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Hydro pneumothorax.jpg|Hydro pneumothorax | |||
File:UOTW 28 - Ultrasound of the Week 1.webm|Ultrasound of the Week 1 | |||
File:UOTW 28 - Ultrasound of the Week 2.webm|Ultrasound of the Week 2 | |||
File:UOTW 28 - Ultrasound of the Week 3.webm|Ultrasound of the Week 3 | |||
File:UOTW 28 - Ultrasound of the Week 4.jpg|Ultrasound of the Week 4 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:41, 20 February 2025
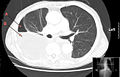
Pleural Empyema is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity, the space between the lung and the inner surface of the chest wall. This condition is usually a complication of pneumonia but can also result from other infections or chest injuries.
Causes
The most common cause of pleural empyema is bacterial infection, often secondary to pneumonia. Other causes include thoracic surgery, chest trauma, and lung abscess. The bacteria involved are usually Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and other Gram-negative bacteria.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pleural empyema include chest pain, cough, fever, shortness of breath, and weight loss. In severe cases, patients may experience tachycardia, cyanosis, and decreased breath sounds on the affected side.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of pleural empyema involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies such as chest X-ray and CT scan, and laboratory tests. Thoracentesis, the removal of fluid from the pleural space, is often performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Treatment
Treatment of pleural empyema involves both medical and surgical interventions. Antibiotics are used to treat the underlying infection, while thoracentesis or chest tube insertion may be performed to drain the empyema. In severe cases, thoracic surgery may be required.
Prognosis
The prognosis of pleural empyema depends on the underlying cause, the patient's overall health, and the timeliness of treatment. With appropriate treatment, most patients recover fully.
See also
Pleural empyema
-
Hydro pneumothorax
-
Ultrasound of the Week 1
-
Ultrasound of the Week 2
-
Ultrasound of the Week 3
-
Ultrasound of the Week 4