Tide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{Ocean-stub}} | {{Ocean-stub}} | ||
{{Physics-stub}} | {{Physics-stub}} | ||
== Tide == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:tide_overview.svg|Tide overview | |||
File:Tidal_circularization_figure1.svg|Tidal circularization figure 1 | |||
File:Tide_and_Moon.jpg|Tide and Moon | |||
File:Tide_St._Simons,_GA_2018.webm|Tide St. Simons, GA 2018 | |||
File:Tide_coming_in_at_St._Simons,_Georgia,_US.webm|Tide coming in at St. Simons, Georgia, US | |||
File:Tide_terms.png|Tide terms | |||
File:Tide_schematic.svg|Tide schematic | |||
File:High_tide_sun_moon_same_side_beginning.png|High tide sun moon same side beginning | |||
File:Low_tide_sun_moon_90_degrees.png|Low tide sun moon 90 degrees | |||
File:High_tide_sun_moon_opposite_side.png|High tide sun moon opposite side | |||
File:Low_tide_sun_moon_270_degrees.png|Low tide sun moon 270 degrees | |||
File:High_tide_sun_moon_same_side_end.png|High tide sun moon same side end | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:45, 23 February 2025
Tide
A tide is the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon, Sun, and the rotation of the Earth. The times and amplitude of tides at a locale are influenced by the alignment of the Sun and Moon, by the pattern of tides in the deep ocean, by the amphidromic systems, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry.
Causes[edit]
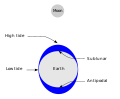
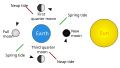
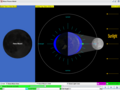
Tides are caused by the gravitational interaction between the Earth and the Moon. The gravitational attraction of the moon causes the oceans to bulge out in the direction of the moon. Another bulge occurs on the opposite side, since the Earth is also being pulled toward the moon (and away from the water on the far side).
Types of Tides[edit]
There are three basic types of tides, all of which occur in pairs: a high tide and a low tide. The semidiurnal tide, where there are two high tides and two low tides each day. The diurnal tide, where there is one high tide and one low tide each day. The mixed tide, where there is a large inequality in the high water heights, low water heights, or both.
Tide Tables[edit]
Tide tables, sometimes called tide charts, are used for tidal prediction and show the daily times and levels of high and low tides, usually for a particular location. Tide heights at intermediate times (between high and low water) can be approximated by using the rule of twelfths or more accurately calculated by using a published tidal curve for the location.
Tidal Power[edit]
Tidal power, also called tidal energy, is a form of hydropower that converts the energy of tides into useful forms of power - mainly electricity. Although not yet widely used, tidal power has potential for future electricity generation.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />

This article is a oceanography stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Tide[edit]
-
Tide overview
-
Tidal circularization figure 1
-
Tide and Moon
-
Tide St. Simons, GA 2018
-
Tide coming in at St. Simons, Georgia, US
-
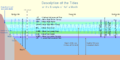
Tide terms
-
Tide schematic
-
High tide sun moon same side beginning
-
Low tide sun moon 90 degrees
-
High tide sun moon opposite side
-
Low tide sun moon 270 degrees
-
High tide sun moon same side end