Insular area: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
[[Category:United States federal territory and statehood legislation]] | [[Category:United States federal territory and statehood legislation]] | ||
{{US-geo-stub}} | {{US-geo-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
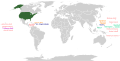
File:US_insular_areas_SVG.svg|Insular_area | |||
File:Ofu_Beach_American_Samoa_US_National_Park_Service.jpg|Ofu Beach, American Samoa | |||
File:Capitolio_de_Puerto_Rico_(28755163211)_(cropped).jpg|Capitolio de Puerto Rico | |||
File:Wake_Island_Lagoon_Paradise_by_Matthew_Piatkowski.jpg|Wake Island Lagoon | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:00, 18 February 2025
Insular area is a term used by the United States to refer to territories that are neither part of one of the fifty states nor federal districts. This term is used to categorize regions that are under the sovereignty of the United States but do not form part of the Union.
Definition[edit]
The term "insular" refers to islands or being characteristic of an island, and thus, insular areas are generally islands or groups of islands. The United States Department of the Interior is responsible for the administration of insular areas.
Types of Insular Areas[edit]
There are three types of insular areas: incorporated territories, unincorporated territories, and Freely Associated States.
Incorporated Territories[edit]
Incorporated territories are regions that have been incorporated into the United States, meaning they are subject to most provisions of the United States Constitution. An example of an incorporated territory is Palmyra Atoll.
Unincorporated Territories[edit]
Unincorporated territories are regions that are controlled by the United States but are not fully subject to all provisions of the U.S. Constitution. Examples of unincorporated territories include Puerto Rico, Guam, and the United States Virgin Islands.
Freely Associated States[edit]
Freely Associated States are sovereign states that have signed a Compact of Free Association with the United States. These states are the Federated States of Micronesia, the Republic of the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of insular areas is determined by the Insular Cases, a series of Supreme Court cases decided in the early 20th century. The Insular Cases established that certain constitutional rights extend to people in insular areas, but not all rights are guaranteed.
See Also[edit]
- Territories of the United States
- Political divisions of the United States
- Organized incorporated territories of the United States
- Unorganized territories of the United States
-
Insular_area
-
Ofu Beach, American Samoa
-
Capitolio de Puerto Rico
-
Wake Island Lagoon