Metynodiol: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{Pharm-stub}} | {{Pharm-stub}} | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
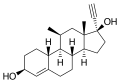
File:Methynodiol.svg|Metynodiol | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:24, 20 February 2025
Metynodiol is a progestin medication which is used in hormone therapy. It is a derivative of progesterone and was introduced for medical use in the 1960s. Metynodiol is taken by mouth and is available only in combination with estrogens.
Pharmacology[edit]
Metynodiol is a progestogen, or an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. It has weak androgenic and glucocorticoid activity and no other important hormonal activity. The medication is a prodrug of norethisterone in the body.
Chemistry[edit]
Metynodiol, also known as 17α-hydroxy-6α-methylprogesterone, is a synthetic pregnane steroid and a derivative of progesterone. It is more specifically a derivative of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and is a member of the class of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives.
History[edit]
Metynodiol was introduced for medical use, specifically in birth control pills, in the 1960s. It is no longer available in the United States, but continues to be used in some other countries.
Society and culture[edit]
Metynodiol is marketed under a variety of brand names including Demulen, Norinyl, and others. It is available only in combination with estrogens.
See also[edit]
-
Metynodiol