Endolymphatic sac tumor: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Post_contrast_T1_weighted_MRI_demonstrates_intense_enhancement_of_both_the_eye_and_the_endolymphatic_sac_tumor..jpg|Post contrast T1 weighted MRI demonstrates intense enhancement of both the eye and the endolymphatic sac tumor. | |||
File:CT_through_the_petrous_ridge_ELST_VHL.jpg|CT through the petrous ridge showing endolymphatic sac tumor in Von Hippel-Lindau disease. | |||
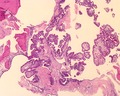
File:Ear_Endolymphatic_Sac_Tumor_H_and_E_Low_power_LDRT.tif|Ear Endolymphatic Sac Tumor H and E Low power. | |||
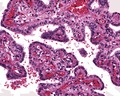
File:Ear_Endolymphatic_Sac_Tumor_H_&_E_High_power_LDRT.tif|Ear Endolymphatic Sac Tumor H & E High power. | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 18 February 2025
Endolymphatic Sac Tumor is a rare, slow-growing tumor that originates in the endolymphatic sac, a part of the inner ear. These tumors are associated with Von Hippel-Lindau disease, a genetic condition that causes tumors and cysts to grow in the body.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of an endolymphatic sac tumor can vary, but often include:
- Hearing loss
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Vertigo (a sense of spinning)
- Facial nerve paralysis
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of an endolymphatic sac tumor typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scan.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment options for endolymphatic sac tumors include:
- Surgery to remove the tumor
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with an endolymphatic sac tumor varies depending on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the individual's overall health.
See Also[edit]
- Von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Inner ear
- Hearing loss
- Tinnitus
- Vertigo
- Facial nerve paralysis
- MRI
- CT scan
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
|
|
|
-
Post contrast T1 weighted MRI demonstrates intense enhancement of both the eye and the endolymphatic sac tumor.
-
CT through the petrous ridge showing endolymphatic sac tumor in Von Hippel-Lindau disease.
-
Ear Endolymphatic Sac Tumor H and E Low power.
-
Ear Endolymphatic Sac Tumor H & E High power.