Male contraceptive: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Open_Vasectomy_.jpeg|Open vasectomy procedure | |||
File:Kondom.jpg|Condom | |||
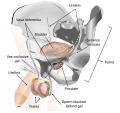
File:Vas-occlusive_Contraception_Diagram.svg|Vas-occlusive contraception diagram | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:35, 18 February 2025
Male contraceptive refers to the methods and devices used by men to prevent pregnancy in their sexual partners. These methods range from temporary solutions such as condoms and withdrawal method, to permanent solutions like vasectomy.
Types of Male Contraceptives[edit]
Condoms[edit]
Condoms are the most common form of male contraceptive. They are a barrier method that prevents sperm from reaching the egg. Condoms also provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Withdrawal Method[edit]
The withdrawal method, also known as "pulling out," involves the man withdrawing his penis from the vagina before ejaculation. This method is less effective than other forms of contraception as it relies on perfect timing and self-control.
Vasectomy[edit]
A vasectomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens, the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the urethra. This procedure is usually permanent, although it can be reversed in some cases.
Effectiveness of Male Contraceptives[edit]
The effectiveness of male contraceptives varies depending on the method used. Condoms, when used correctly, have a success rate of around 98%. The withdrawal method, on the other hand, has a lower success rate of around 78%. Vasectomies are over 99% effective.
Future Developments[edit]
Research is ongoing into new forms of male contraceptives, including hormonal methods and non-hormonal methods such as gels and injections. These new methods aim to provide men with more contraceptive options and to increase the overall effectiveness of male contraception.