Liver tumor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Liver_tumor_types_in_adults_by_relative_incidence.png|Liver tumor types in adults by relative incidence | |||
File:Ultrasound_Scan_ND_1230124453_1300210.png|Ultrasound scan of liver tumor | |||
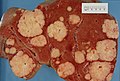
File:Secondary_tumor_deposits_in_the_liver_from_a_primary_cancer_of_the_pancreas.jpg|Secondary tumor deposits in the liver from a primary cancer of the pancreas | |||
File:Late_arterial_and_portal_venous_phase_CT_of_focal_nodular_hyperplasia.jpg|Late arterial and portal venous phase CT of focal nodular hyperplasia | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 11:27, 18 February 2025
Liver tumor is a growth or mass in the liver that can either be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The liver is one of the largest organs in the body and is responsible for filtering harmful substances from the blood, storing nutrients and vitamins, and aiding in digestion.
Types of Liver Tumors
There are several types of liver tumors, including:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): This is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults. It begins in the cells of the liver.
- Cholangiocarcinoma: This type of liver cancer starts in the small, tube-like bile ducts within the liver.
- Liver angiosarcoma: A rare form of liver cancer, liver angiosarcoma begins in the blood vessels of the liver and grows very quickly.
- Hepatoblastoma: This is a rare type of liver cancer that usually affects children aged 3 and under.
Symptoms
Symptoms of liver tumors can vary, but may include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Loss of appetite or unexplained weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- General fatigue or weakness
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of liver tumors typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound. In some cases, a biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment options for liver tumors depend on the type and stage of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. Options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these.
See Also
References
<references />