Hangman's fracture: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Hangman's fracture == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:CT of hangman's fracture.jpg|CT of Hangman's fracture | |||
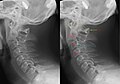
File:Hangman's fracture.JPG|Hangman's fracture | |||
File:Hangman's fracture.jpg|Hangman's fracture | |||
File:Incidence According to Age Group in the USA during 2010.png|Incidence According to Age Group in the USA during 2010 | |||
File:Trend of Hospital Charges and Number of Discharges.png|Trend of Hospital Charges and Number of Discharges | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:00, 20 February 2025
Hangman's fracture is a specific type of cervical fracture that involves the second cervical vertebra (C2). It is a serious injury that can lead to severe neurological complications or death. The fracture is named after the method of execution by hanging, as the mechanism of injury is similar.
Causes
Hangman's fractures are typically caused by extreme hyperextension of the neck, often as a result of high-speed motor vehicle accidents or falls from a significant height. They can also occur as a result of attempted suicide by hanging, although this is less common.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a hangman's fracture can vary depending on the severity of the injury. They may include:
- Severe neck pain
- Difficulty moving the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Numbness or weakness in the limbs
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a hangman's fracture typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs. The fracture is characterized by a break in the pars interarticularis of C2 on both sides.
Treatment
Treatment for a hangman's fracture depends on the severity of the fracture and the patient's overall health. It may involve:
- Immobilization with a cervical collar or halo vest
- Pain management with medications
- Surgery to stabilize the spine
Prognosis
The prognosis for a hangman's fracture depends on the severity of the injury and the patient's overall health. With appropriate treatment, some patients may make a full recovery. However, severe fractures can result in long-term complications such as chronic pain, difficulty swallowing or speaking, and neurological problems.