Adrenergic neuron blockers: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
[[Category:Adrenergic drugs]] | [[Category:Adrenergic drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Antihypertensive agents]] | [[Category:Antihypertensive agents]] | ||
<gallery caption="Adrenergic_neuron_blockers"> | |||
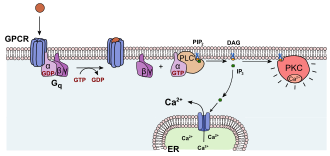
File:Activation_protein_kinase_C.svg|Activation of protein kinase C | |||
File:Copd_2010.jpg|Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) illustration | |||
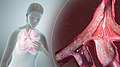
File:Respiratory_tract.jpg|Diagram of the human respiratory tract | |||
File:Orthostatic_Hypertension_demonstration.gif|Demonstration of orthostatic hypertension | |||
File:Asthma_attack-illustration_NIH.jpg|Illustration of an asthma attack | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:58, 18 February 2025
Adrenergic Neuron Blockers[edit]
Adrenergic neuron blockers are a class of medications that inhibit the function of adrenergic neurons, which are responsible for the release of norepinephrine and epinephrine in the sympathetic nervous system. These blockers are primarily used to manage hypertension and certain types of cardiac arrhythmias.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Adrenergic neuron blockers work by preventing the release of norepinephrine from the nerve terminals. This is achieved through various mechanisms, such as inhibiting the storage of norepinephrine in synaptic vesicles or blocking the action of calcium channels that facilitate neurotransmitter release. By reducing the availability of norepinephrine, these drugs decrease the stimulation of adrenergic receptors, leading to a reduction in blood pressure and heart rate.
Clinical Uses[edit]
Adrenergic neuron blockers are used in the treatment of:
- Hypertension: By reducing peripheral vascular resistance and cardiac output, these drugs help lower blood pressure.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: They can stabilize heart rhythms by reducing sympathetic stimulation.
- Heart failure: In some cases, they are used to decrease the workload on the heart.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of adrenergic neuron blockers include:
- Orthostatic hypotension: A sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing, which can lead to dizziness and fainting.
- Bradycardia: A slower than normal heart rate.
- Nasal congestion: Due to vasodilation in the nasal passages.
- Fatigue and depression: Resulting from reduced sympathetic activity.
Related Conditions[edit]
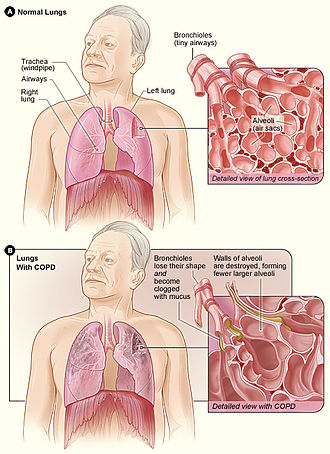
Adrenergic neuron blockers may have implications in the management of respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, caution is advised as these drugs can potentially exacerbate respiratory symptoms by reducing bronchodilation.
Related Pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Diagram of the respiratory tract, which can be affected by adrenergic neuron blockers.
-
Demonstration of orthostatic hypotension, a common side effect.
-
Illustration of an asthma attack, a condition that may be influenced by adrenergic neuron blockers.
- Adrenergic_neuron_blockers
-
Activation of protein kinase C
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) illustration
-
Diagram of the human respiratory tract
-
Demonstration of orthostatic hypertension
-
Illustration of an asthma attack