Verbal fluency test: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Verbal Fluency Test == | |||
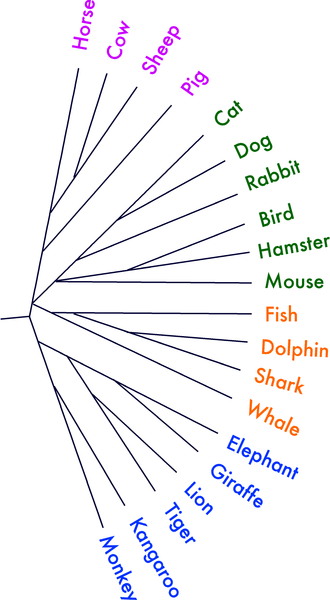
[[File:Animal_addtree_age7_nocat.png|thumb|right|Diagram illustrating the animal category fluency task.]] | |||
The '''verbal fluency test''' is a neuropsychological assessment used to measure an individual's ability to generate words fluently. It is commonly used to assess cognitive function, particularly in the domains of language and executive function. The test is often employed in clinical settings to evaluate patients with neurological conditions, such as [[dementia]], [[stroke]], or [[traumatic brain injury]]. | |||
== | == Types of Verbal Fluency Tests == | ||
There are two primary types of verbal fluency tests: '''phonemic fluency''' and '''semantic fluency'''. | |||
== | === Phonemic Fluency === | ||
In the phonemic fluency test, individuals are asked to produce as many words as possible that begin with a given letter, such as "F," "A," or "S," within a set time limit, usually one minute. This task assesses the ability to retrieve words based on phonological cues and requires executive control to avoid repetitions and rule violations. | |||
=== Semantic Fluency === | |||
In the semantic fluency test, individuals are asked to generate words belonging to a specific category, such as "animals" or "fruits," within a time limit. This task evaluates the ability to access and retrieve words based on semantic memory and is often used to assess the integrity of the [[temporal lobe]] and [[semantic memory]]. | |||
== Clinical Significance == | |||
{{ | Verbal fluency tests are sensitive to a variety of neurological conditions. Poor performance on these tests can indicate deficits in language, executive function, or memory. For example, individuals with [[Alzheimer's disease]] often show impaired semantic fluency due to degeneration of the temporal lobes, while those with [[Parkinson's disease]] may exhibit reduced phonemic fluency due to frontal lobe dysfunction. | ||
== Administration and Scoring == | |||
The verbal fluency test is typically administered in a quiet environment with minimal distractions. The examiner provides clear instructions and records the number of correct words generated, as well as any repetitions or rule violations. Scoring involves counting the total number of valid words produced, with adjustments made for errors. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Neuropsychological test]] | |||
* [[Executive functions]] | |||
* [[Language processing]] | |||
* [[Cognitive assessment]] | |||
{{Neuropsychology}} | |||
[[Category:Neuropsychological tests]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:28, 16 February 2025
Verbal Fluency Test[edit]
The verbal fluency test is a neuropsychological assessment used to measure an individual's ability to generate words fluently. It is commonly used to assess cognitive function, particularly in the domains of language and executive function. The test is often employed in clinical settings to evaluate patients with neurological conditions, such as dementia, stroke, or traumatic brain injury.
Types of Verbal Fluency Tests[edit]
There are two primary types of verbal fluency tests: phonemic fluency and semantic fluency.
Phonemic Fluency[edit]
In the phonemic fluency test, individuals are asked to produce as many words as possible that begin with a given letter, such as "F," "A," or "S," within a set time limit, usually one minute. This task assesses the ability to retrieve words based on phonological cues and requires executive control to avoid repetitions and rule violations.
Semantic Fluency[edit]
In the semantic fluency test, individuals are asked to generate words belonging to a specific category, such as "animals" or "fruits," within a time limit. This task evaluates the ability to access and retrieve words based on semantic memory and is often used to assess the integrity of the temporal lobe and semantic memory.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Verbal fluency tests are sensitive to a variety of neurological conditions. Poor performance on these tests can indicate deficits in language, executive function, or memory. For example, individuals with Alzheimer's disease often show impaired semantic fluency due to degeneration of the temporal lobes, while those with Parkinson's disease may exhibit reduced phonemic fluency due to frontal lobe dysfunction.
Administration and Scoring[edit]
The verbal fluency test is typically administered in a quiet environment with minimal distractions. The examiner provides clear instructions and records the number of correct words generated, as well as any repetitions or rule violations. Scoring involves counting the total number of valid words produced, with adjustments made for errors.
Related Pages[edit]
| Neuropsychology |
|---|
|
|