High-frequency ventilation: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Bunnell_Life_Pulse.jpg|Bunnell Life Pulse | |||
File:HFJV_Flow.jpg|HFJV Flow | |||
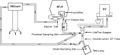
File:Inhaled_Nitric_Oxide_(iNO)_Delivery_with_High-frequency_Jet_Ventilation_(HFJV).jpg|Inhaled Nitric Oxide (iNO) Delivery with High-frequency Jet Ventilation (HFJV) | |||
File:HFOV_3100A.jpg|HFOV 3100A | |||
File:Oscillator_3100A_2012_diagram.jpg|Oscillator 3100A 2012 diagram | |||
File:Drawing_of_air_movement_during_high_frequency_oscillation_ventilation.png|Drawing of air movement during high frequency oscillation ventilation | |||
File:HFOV_Tidal_volume_versus_power_setting.jpg|HFOV Tidal volume versus power setting | |||
File:HFOV_Tidal_volume_versus_frequency_hz.jpg|HFOV Tidal volume versus frequency hz | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:23, 18 February 2025
High-frequency ventilation (HFV) is a type of mechanical ventilation which utilizes respiratory rates that are significantly higher than those observed in conventional mechanical ventilation. HFV is a sophisticated method of ventilatory support, primarily used in neonatal and pediatric intensive care units, but also applicable in adult critical care settings under specific circumstances. This form of ventilation is particularly beneficial for patients with lung injury or those requiring minimal lung movement to facilitate healing, as it can improve oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal while reducing ventilator-induced lung injury.
Types of High-frequency Ventilation[edit]
There are several types of HFV, each with unique mechanisms of action:
- High-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) - Utilizes a constant distending pressure to the lungs with small pressure variations at a high frequency (usually > 150 breaths per minute), facilitating gas exchange.
- High-frequency jet ventilation (HFJV) - Delivers small bursts of gas into the lungs at high frequencies through a small cannula positioned within the trachea.
- High-frequency percussive ventilation (HFPV) - Combines conventional mechanical breaths with high-frequency percussive mini-bursts of air.
Indications[edit]
High-frequency ventilation may be indicated for patients with:
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
- Air leak syndromes such as pneumothorax
- Pulmonary hemorrhage
- Conditions requiring reduced pulmonary blood flow or minimal lung movement
Advantages[edit]
The primary advantages of HFV include:
- Reduced risk of ventilator-induced lung injury due to lower tidal volumes
- Improved oxygenation and CO2 removal
- Potential for better lung recruitment with minimal barotrauma
Disadvantages[edit]
Despite its benefits, HFV has several disadvantages:
- Complexity of the ventilation mode requiring specialized training and experience
- Potential for impaired hemodynamics due to high intrathoracic pressures
- Difficulty in monitoring and adjusting ventilator settings due to the unique nature of the ventilation
Clinical Considerations[edit]
When initiating HFV, careful consideration must be given to the patient's condition, including lung compliance, gas exchange requirements, and hemodynamic stability. Monitoring involves not only traditional parameters such as oxygen saturation and blood gases but also specific considerations related to the mode of HFV being used.
Conclusion[edit]
High-frequency ventilation represents an advanced ventilatory strategy that can offer significant benefits to critically ill patients with specific respiratory conditions. However, its application requires a thorough understanding of its mechanisms, indications, and potential complications. As research evolves, HFV may become more widely adopted across different patient populations and clinical scenarios.
-
Bunnell Life Pulse
-
HFJV Flow
-
Inhaled Nitric Oxide (iNO) Delivery with High-frequency Jet Ventilation (HFJV)
-
HFOV 3100A
-
Oscillator 3100A 2012 diagram
-
Drawing of air movement during high frequency oscillation ventilation
-
HFOV Tidal volume versus power setting
-
HFOV Tidal volume versus frequency hz