Hyperthymic temperament: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hyperthymic temperament | |||
| image = [[File:Hyperthymia.png|250px]] | |||
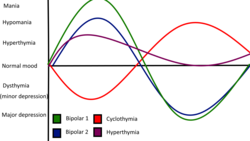
| caption = Illustration of hyperthymic temperament | |||
| field = [[Psychiatry]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Persistent positive mood]], [[high energy]], [[sociability]], [[talkativeness]] | |||
| complications = [[Bipolar disorder]], [[substance use disorder]] | |||
| onset = [[Adolescence]] or [[early adulthood]] | |||
| duration = [[Chronic]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic predisposition]], [[environmental factors]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history of mood disorders]] | |||
| differential = [[Cyclothymic disorder]], [[bipolar disorder]], [[attention deficit hyperactivity disorder]] | |||
| treatment = [[Psychotherapy]], [[mood stabilizers]] | |||
| frequency = Unknown | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|Overview of hyperthymic temperament}} | |||
A '''hyperthymic temperament''' is characterized by an excessively positive mood and disposition. Individuals with this temperament tend to be highly energetic, sociable, and optimistic. This temperament is considered one of the [[temperament]] types in [[psychology]] and is often associated with [[bipolar disorder]] and other [[mood disorders]]. | |||
==Characteristics== | ==Characteristics== | ||
People with a hyperthymic temperament often exhibit the following traits: | |||
* | * '''Increased energy levels''': They tend to have more energy than the average person, often leading to high levels of productivity and activity. | ||
* | * '''Sociability''': Individuals are typically very outgoing and enjoy social interactions. | ||
* Reduced need for sleep | * '''Optimism''': They generally have a positive outlook on life and are resilient in the face of adversity. | ||
* '''Talkativeness''': A tendency to engage in conversation frequently and enthusiastically. | |||
* '''Impulsivity''': They may act on impulse without considering the consequences. | |||
* '''Reduced need for sleep''': Often requiring less sleep than average, which can contribute to their high energy levels. | |||
==Clinical Implications== | |||
While a hyperthymic temperament can be advantageous in many situations, it can also pose challenges. The high energy and impulsivity associated with this temperament can lead to difficulties in maintaining stable relationships and adhering to long-term goals. In some cases, it may predispose individuals to [[bipolar disorder]], particularly [[bipolar II disorder]], where hypomanic episodes are more common. | |||
== | ==Management== | ||
Management of a hyperthymic temperament involves recognizing the potential for mood disorders and implementing strategies to maintain balance. This may include: | |||
* '''Psychotherapy''': Engaging in [[cognitive behavioral therapy]] (CBT) to develop coping strategies. | |||
== | * '''Lifestyle modifications''': Ensuring adequate sleep, regular exercise, and a balanced diet. | ||
* '''Medication''': In some cases, mood stabilizers or other medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms. | |||
==See also== | |||
* [[Temperament]] | |||
* [[Bipolar disorder]] | |||
* [[Mood disorder]] | |||
== | * [[Cognitive behavioral therapy]] | ||
[[Category:Temperament]] | |||
[[Category:Psychology]] | |||
[[Category:Mood disorders]] | [[Category:Mood disorders]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:53, 7 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hyperthymic temperament | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Persistent positive mood, high energy, sociability, talkativeness |
| Complications | Bipolar disorder, substance use disorder |
| Onset | Adolescence or early adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic predisposition, environmental factors |
| Risks | Family history of mood disorders |
| Diagnosis | N/A |
| Differential diagnosis | Cyclothymic disorder, bipolar disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Psychotherapy, mood stabilizers |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Unknown |
| Deaths | N/A |
Overview of hyperthymic temperament
A hyperthymic temperament is characterized by an excessively positive mood and disposition. Individuals with this temperament tend to be highly energetic, sociable, and optimistic. This temperament is considered one of the temperament types in psychology and is often associated with bipolar disorder and other mood disorders.
Characteristics[edit]
People with a hyperthymic temperament often exhibit the following traits:
- Increased energy levels: They tend to have more energy than the average person, often leading to high levels of productivity and activity.
- Sociability: Individuals are typically very outgoing and enjoy social interactions.
- Optimism: They generally have a positive outlook on life and are resilient in the face of adversity.
- Talkativeness: A tendency to engage in conversation frequently and enthusiastically.
- Impulsivity: They may act on impulse without considering the consequences.
- Reduced need for sleep: Often requiring less sleep than average, which can contribute to their high energy levels.
Clinical Implications[edit]
While a hyperthymic temperament can be advantageous in many situations, it can also pose challenges. The high energy and impulsivity associated with this temperament can lead to difficulties in maintaining stable relationships and adhering to long-term goals. In some cases, it may predispose individuals to bipolar disorder, particularly bipolar II disorder, where hypomanic episodes are more common.
Management[edit]
Management of a hyperthymic temperament involves recognizing the potential for mood disorders and implementing strategies to maintain balance. This may include:
- Psychotherapy: Engaging in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to develop coping strategies.
- Lifestyle modifications: Ensuring adequate sleep, regular exercise, and a balanced diet.
- Medication: In some cases, mood stabilizers or other medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms.