Thiotrisescaline: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A psychedelic compound related to mescaline}} | |||
{{Psychedelic drug}} | |||
'''Thiotrisescaline''' (also known as '''TTE''') is a synthetic psychedelic compound that belongs to the phenethylamine class. It is chemically related to [[mescaline]], a naturally occurring psychedelic found in certain cacti. Thiotrisescaline is known for its psychoactive effects, which are similar to those of other psychedelics, such as [[LSD]] and [[psilocybin]]. | |||
Thiotrisescaline | |||
==Chemical Structure and Properties== | |||
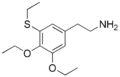
Thiotrisescaline is a member of the [[phenethylamine]] family, characterized by its core structure of a phenyl ring bound to an amino group through an ethyl chain. The chemical structure of thiotrisescaline is distinguished by the presence of three methoxy groups and a thioether group attached to the phenyl ring. This structural modification is responsible for its unique pharmacological properties. | |||
==Pharmacology== | ==Pharmacology== | ||
Thiotrisescaline acts primarily as a [[serotonin receptor]] agonist, particularly at the 5-HT<sub>2A</sub> receptor, which is believed to be the primary site of action for its psychedelic effects. The activation of these receptors leads to altered perception, mood, and cognition, which are characteristic of the psychedelic experience. | |||
==Effects== | ==Effects== | ||
The effects of | The effects of thiotrisescaline are similar to those of other psychedelics, including: | ||
* Altered sensory perception | |||
* Enhanced introspection | |||
* Emotional variability | |||
* Visual and auditory hallucinations | |||
The onset of effects typically occurs within 30 to 60 minutes after ingestion, with the peak experience lasting 4 to 6 hours. The total duration of effects can last up to 12 hours. | |||
==Safety and Toxicity== | |||
As with many psychedelics, the safety profile of thiotrisescaline is not well-established due to limited research. However, it is generally considered to have a low toxicity profile when used in moderate doses. Potential risks include psychological distress, anxiety, and the possibility of triggering latent mental health disorders. | |||
==Legal Status== | ==Legal Status== | ||
The legal status of | The legal status of thiotrisescaline varies by country. In many jurisdictions, it is classified as a controlled substance due to its structural similarity to other regulated psychedelics. Users should be aware of the legal implications of possessing or using thiotrisescaline in their region. | ||
==Related Compounds== | |||
Thiotrisescaline is part of a broader class of compounds known as [[substituted phenethylamines]], which includes other psychedelics such as: | |||
* [[Mescaline]] | |||
* [[2C-B]] | |||
* [[2C-I]] | |||
These compounds share similar mechanisms of action and effects, though each has unique properties and potency. | |||
==Research and Applications== | |||
Research into thiotrisescaline and related compounds is ongoing, with interest in their potential therapeutic applications. Psychedelics are being studied for their efficacy in treating conditions such as [[depression]], [[anxiety]], and [[post-traumatic stress disorder]] (PTSD). | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Psychedelic therapy]] | |||
* [[Serotonin receptor]] | |||
* [[Phenethylamine]] | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Mescaline]] | * [[Mescaline]] | ||
* [[Psychedelic drug]] | * [[Psychedelic drug]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Serotonin]] | ||
[[Category:Psychedelic phenethylamines]] | [[Category:Psychedelic phenethylamines]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Serotonin receptor agonists]] | ||
==Thiotrisescaline== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:3-T-TRIS.png|3-T-TRIS | |||
File:4-T-TRIS.png|4-T-TRIS | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:01, 3 March 2025
A psychedelic compound related to mescaline
Thiotrisescaline (also known as TTE) is a synthetic psychedelic compound that belongs to the phenethylamine class. It is chemically related to mescaline, a naturally occurring psychedelic found in certain cacti. Thiotrisescaline is known for its psychoactive effects, which are similar to those of other psychedelics, such as LSD and psilocybin.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
Thiotrisescaline is a member of the phenethylamine family, characterized by its core structure of a phenyl ring bound to an amino group through an ethyl chain. The chemical structure of thiotrisescaline is distinguished by the presence of three methoxy groups and a thioether group attached to the phenyl ring. This structural modification is responsible for its unique pharmacological properties.
Pharmacology[edit]
Thiotrisescaline acts primarily as a serotonin receptor agonist, particularly at the 5-HT2A receptor, which is believed to be the primary site of action for its psychedelic effects. The activation of these receptors leads to altered perception, mood, and cognition, which are characteristic of the psychedelic experience.
Effects[edit]
The effects of thiotrisescaline are similar to those of other psychedelics, including:
- Altered sensory perception
- Enhanced introspection
- Emotional variability
- Visual and auditory hallucinations
The onset of effects typically occurs within 30 to 60 minutes after ingestion, with the peak experience lasting 4 to 6 hours. The total duration of effects can last up to 12 hours.
Safety and Toxicity[edit]
As with many psychedelics, the safety profile of thiotrisescaline is not well-established due to limited research. However, it is generally considered to have a low toxicity profile when used in moderate doses. Potential risks include psychological distress, anxiety, and the possibility of triggering latent mental health disorders.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of thiotrisescaline varies by country. In many jurisdictions, it is classified as a controlled substance due to its structural similarity to other regulated psychedelics. Users should be aware of the legal implications of possessing or using thiotrisescaline in their region.
Related Compounds[edit]
Thiotrisescaline is part of a broader class of compounds known as substituted phenethylamines, which includes other psychedelics such as:
These compounds share similar mechanisms of action and effects, though each has unique properties and potency.
Research and Applications[edit]
Research into thiotrisescaline and related compounds is ongoing, with interest in their potential therapeutic applications. Psychedelics are being studied for their efficacy in treating conditions such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
See Also[edit]
Related pages[edit]
Thiotrisescaline[edit]
-
3-T-TRIS
-
4-T-TRIS