Etabonate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Etabonate == | |||
[[File:Etabonate_skeletal.svg|thumb|right|200px|Skeletal structure of Etabonate]] | |||
'''Etabonate''' is a chemical compound that is often used as a [[prodrug]] moiety in pharmaceutical formulations. It is a derivative of [[ethanol]] and is commonly used to enhance the [[bioavailability]] of certain [[medications]]. | |||
== Chemical Structure == | |||
== | Etabonate is characterized by its [[skeletal structure]], which includes an [[ester]] linkage. The presence of the etabonate group in a drug molecule can significantly alter its [[pharmacokinetics]], allowing for improved absorption and distribution within the body. | ||
== Pharmacological Use == | |||
In the field of [[pharmacology]], etabonate is utilized to modify the [[solubility]] and [[stability]] of active pharmaceutical ingredients. By attaching an etabonate group to a drug, researchers can create a [[prodrug]] that is more easily absorbed when administered orally. Once inside the body, the etabonate group is typically cleaved by [[enzymes]], releasing the active drug. | |||
== Examples of Etabonate Prodrugs == | |||
Several medications use the etabonate moiety to improve their therapeutic profiles. These include certain [[corticosteroids]] and [[antibiotics]], where the etabonate group helps in achieving a more favorable [[pharmacokinetic]] profile. | |||
== Mechanism of Action == | |||
The mechanism by which etabonate enhances drug delivery involves its conversion to the active drug form in the body. This conversion is often facilitated by [[esterases]], which are enzymes that hydrolyze ester bonds. The release of the active drug from its etabonate form allows for targeted action at the site of interest. | |||
== Advantages of Etabonate == | |||
The use of etabonate in drug formulations offers several advantages: | |||
* '''Improved Solubility''': Etabonate can increase the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs, enhancing their absorption. | |||
* '''Enhanced Stability''': It can protect the active drug from premature degradation. | |||
* '''Controlled Release''': The prodrug approach allows for controlled release of the active drug, potentially reducing side effects. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Prodrug]] | * [[Prodrug]] | ||
* [[Pharmacokinetics]] | |||
* [[Ester]] | * [[Ester]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Bioavailability]] | ||
[[Category:Pharmacology]] | |||
[[Category:Chemical compounds]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:33, 15 February 2025
Etabonate[edit]
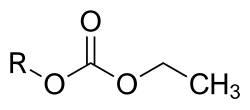
Etabonate is a chemical compound that is often used as a prodrug moiety in pharmaceutical formulations. It is a derivative of ethanol and is commonly used to enhance the bioavailability of certain medications.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Etabonate is characterized by its skeletal structure, which includes an ester linkage. The presence of the etabonate group in a drug molecule can significantly alter its pharmacokinetics, allowing for improved absorption and distribution within the body.
Pharmacological Use[edit]
In the field of pharmacology, etabonate is utilized to modify the solubility and stability of active pharmaceutical ingredients. By attaching an etabonate group to a drug, researchers can create a prodrug that is more easily absorbed when administered orally. Once inside the body, the etabonate group is typically cleaved by enzymes, releasing the active drug.
Examples of Etabonate Prodrugs[edit]
Several medications use the etabonate moiety to improve their therapeutic profiles. These include certain corticosteroids and antibiotics, where the etabonate group helps in achieving a more favorable pharmacokinetic profile.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
The mechanism by which etabonate enhances drug delivery involves its conversion to the active drug form in the body. This conversion is often facilitated by esterases, which are enzymes that hydrolyze ester bonds. The release of the active drug from its etabonate form allows for targeted action at the site of interest.
Advantages of Etabonate[edit]
The use of etabonate in drug formulations offers several advantages:
- Improved Solubility: Etabonate can increase the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs, enhancing their absorption.
- Enhanced Stability: It can protect the active drug from premature degradation.
- Controlled Release: The prodrug approach allows for controlled release of the active drug, potentially reducing side effects.