Ethyl dirazepate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Skeletal muscle relaxants]] | [[Category:Skeletal muscle relaxants]] | ||
{{Pharma-stub}} | {{Pharma-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
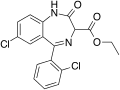
File:Ethyl_dirazepate.svg|Ethyl dirazepate chemical structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 20:53, 16 March 2025
Ethyl dirazepate is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.
Chemistry[edit]
Ethyl dirazepate, also known as ethyl 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-ylacetate, is a member of the class of compounds known as benzodiazepines. These are organic compounds containing a benzene ring fused to either isomers of diazepine(unsaturated seven-member heterocycle with two nitrogen atoms replacing two carbon atoms).
Pharmacology[edit]
Ethyl dirazepate acts by binding to the GABA_A receptor, enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA). By increasing the GABA inhibition and reducing the excitability of neurons, ethyl dirazepate has a calming effect on the nervous system.
Medical uses[edit]
Ethyl dirazepate is used for the treatment of anxiety disorders, insomnia, and for the control of epileptic seizures. It may also be used as a premedication for medical or surgical procedures where anxiety may be a factor.
Side effects[edit]
Like other benzodiazepines, ethyl dirazepate can cause physical dependence and addiction. Withdrawal symptoms may occur if the medication is stopped abruptly. Other side effects may include drowsiness, confusion, dizziness, and ataxia.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
-
Ethyl dirazepate chemical structure