Humoral immune deficiency: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Humoral immune deficiency | |||
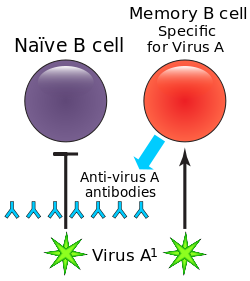
| image = [[File:Original_antigenic_sin.svg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Diagram illustrating the concept of original antigenic sin, which can be related to immune deficiencies. | |||
| field = [[Immunology]] | |||
| symptoms = Recurrent [[bacterial infections]], [[sinusitis]], [[pneumonia]], [[otitis media]] | |||
| complications = [[Chronic lung disease]], [[autoimmune disorders]] | |||
| onset = Usually in [[childhood]] | |||
| duration = [[Chronic (medicine)|Chronic]] | |||
| causes = Genetic mutations affecting [[B cells]] or [[antibody]] production | |||
| risks = Family history of immune deficiencies | |||
| diagnosis = [[Serum immunoglobulin]] levels, [[flow cytometry]] | |||
| differential = [[Common variable immunodeficiency]], [[X-linked agammaglobulinemia]] | |||
| treatment = [[Immunoglobulin therapy]], [[antibiotics]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depending on severity and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Human_B_Lymphocyte_-_NIAID.jpg|Human B Lymphocyte|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Humoral immune deficiency''' is a type of [[immunodeficiency]] that primarily affects the [[B cells]] of the [[immune system]]. This condition is characterized by a decreased or absent production of [[antibodies]], which are crucial for fighting off infections and diseases. | '''Humoral immune deficiency''' is a type of [[immunodeficiency]] that primarily affects the [[B cells]] of the [[immune system]]. This condition is characterized by a decreased or absent production of [[antibodies]], which are crucial for fighting off infections and diseases. | ||
== Introduction == | |||
== | |||
The [[immune system]] is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. The humoral immune response is one part of this system, and it involves the production of antibodies by B cells. These antibodies are specific proteins that can recognize and neutralize specific pathogens. | The [[immune system]] is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. The humoral immune response is one part of this system, and it involves the production of antibodies by B cells. These antibodies are specific proteins that can recognize and neutralize specific pathogens. | ||
In individuals with humoral immune deficiency, the B cells are either not produced in sufficient numbers, or they are unable to produce antibodies effectively. This can lead to an increased susceptibility to infections, particularly those caused by bacteria and viruses. | In individuals with humoral immune deficiency, the B cells are either not produced in sufficient numbers, or they are unable to produce antibodies effectively. This can lead to an increased susceptibility to infections, particularly those caused by bacteria and viruses. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Humoral immune deficiency can be caused by a variety of factors. Some individuals are born with the condition due to genetic mutations, making it a type of [[primary immunodeficiency]]. Other times, the condition can be acquired later in life due to certain diseases or treatments, such as [[chemotherapy]], making it a type of [[secondary immunodeficiency]]. | Humoral immune deficiency can be caused by a variety of factors. Some individuals are born with the condition due to genetic mutations, making it a type of [[primary immunodeficiency]]. Other times, the condition can be acquired later in life due to certain diseases or treatments, such as [[chemotherapy]], making it a type of [[secondary immunodeficiency]]. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of humoral immune deficiency can vary widely, but they often include frequent infections, particularly of the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. Other symptoms can include fatigue, weight loss, and an overall feeling of being unwell. | The symptoms of humoral immune deficiency can vary widely, but they often include frequent infections, particularly of the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. Other symptoms can include fatigue, weight loss, and an overall feeling of being unwell. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of humoral immune deficiency typically involves a series of tests to evaluate the function of the immune system. These can include blood tests to measure the levels of antibodies in the blood, as well as tests to assess the function of the B cells. | Diagnosis of humoral immune deficiency typically involves a series of tests to evaluate the function of the immune system. These can include blood tests to measure the levels of antibodies in the blood, as well as tests to assess the function of the B cells. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for humoral immune deficiency often involves [[immunoglobulin therapy]], which involves the administration of antibodies to help boost the immune system. Other treatments can include antibiotics to treat infections, as well as lifestyle changes to help reduce the risk of infection. | Treatment for humoral immune deficiency often involves [[immunoglobulin therapy]], which involves the administration of antibodies to help boost the immune system. Other treatments can include antibiotics to treat infections, as well as lifestyle changes to help reduce the risk of infection. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Primary immunodeficiency]] | * [[Primary immunodeficiency]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 36: | ||
* [[Antibodies]] | * [[Antibodies]] | ||
* [[Immunoglobulin therapy]] | * [[Immunoglobulin therapy]] | ||
[[Category:Immunodeficiency]] | [[Category:Immunodeficiency]] | ||
[[Category:Immune system disorders]] | [[Category:Immune system disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:11, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Humoral immune deficiency | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Recurrent bacterial infections, sinusitis, pneumonia, otitis media |
| Complications | Chronic lung disease, autoimmune disorders |
| Onset | Usually in childhood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutations affecting B cells or antibody production |
| Risks | Family history of immune deficiencies |
| Diagnosis | Serum immunoglobulin levels, flow cytometry |
| Differential diagnosis | Common variable immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Immunoglobulin therapy, antibiotics |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depending on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Humoral immune deficiency is a type of immunodeficiency that primarily affects the B cells of the immune system. This condition is characterized by a decreased or absent production of antibodies, which are crucial for fighting off infections and diseases.
Introduction[edit]
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. The humoral immune response is one part of this system, and it involves the production of antibodies by B cells. These antibodies are specific proteins that can recognize and neutralize specific pathogens. In individuals with humoral immune deficiency, the B cells are either not produced in sufficient numbers, or they are unable to produce antibodies effectively. This can lead to an increased susceptibility to infections, particularly those caused by bacteria and viruses.
Causes[edit]
Humoral immune deficiency can be caused by a variety of factors. Some individuals are born with the condition due to genetic mutations, making it a type of primary immunodeficiency. Other times, the condition can be acquired later in life due to certain diseases or treatments, such as chemotherapy, making it a type of secondary immunodeficiency.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of humoral immune deficiency can vary widely, but they often include frequent infections, particularly of the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. Other symptoms can include fatigue, weight loss, and an overall feeling of being unwell.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of humoral immune deficiency typically involves a series of tests to evaluate the function of the immune system. These can include blood tests to measure the levels of antibodies in the blood, as well as tests to assess the function of the B cells.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for humoral immune deficiency often involves immunoglobulin therapy, which involves the administration of antibodies to help boost the immune system. Other treatments can include antibiotics to treat infections, as well as lifestyle changes to help reduce the risk of infection.
See also[edit]
