Tissue factor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
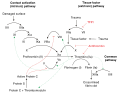
File:Coagulation_full.svg|Diagram of the coagulation cascade | |||
File:Tissue_factor.png|Structure of Tissue Factor | |||
File:Fibrin-nach-Thromboplastin.jpg|Fibrin formation after thromboplastin activation | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:06, 18 February 2025
Testosterone nicotinate is a synthetic anabolic steroid and a derivative of testosterone. It is an ester of testosterone with nicotinic acid and is used in the treatment of hypogonadism and other conditions associated with low testosterone levels.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Testosterone nicotinate is a testosterone molecule with a nicotinic acid ester attached to the 17-beta hydroxyl group. This modification allows the drug to be released slowly into the body after injection, providing a sustained release of testosterone.
Pharmacology[edit]
Testosterone nicotinate is administered by intramuscular injection. It is absorbed into the bloodstream and then converted into testosterone by the body. The testosterone then binds to androgen receptors in target tissues, exerting its effects.
Clinical Uses[edit]
Testosterone nicotinate is used in the treatment of conditions associated with low testosterone levels, including male hypogonadism, delayed puberty in boys, and certain types of breast cancer in women. It may also be used to improve physical performance and body composition in certain patient populations.
Side Effects[edit]
Like all anabolic steroids, testosterone nicotinate can have side effects. These may include acne, hair loss, increased body hair growth, changes in sexual desire, and mood changes. More serious side effects can include liver damage, cardiovascular disease, and psychiatric disorders.