Immunohistochemistry: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category:Medical Techniques]] | [[Category:Medical Techniques]] | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
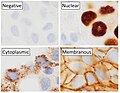
File:Main_staining_patterns_on_immunohistochemistry.jpg|Main staining patterns on immunohistochemistry | |||
File:HSP_IF_IgA.jpg|HSP IF IgA | |||
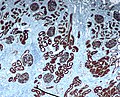
File:Immunohistochemistry_for_p16_in_uterine_papillary_serous_adenocarcinoma_showing_both_nuclear_and_cytoplasmic_staining.jpg|Immunohistochemistry for p16 in uterine papillary serous adenocarcinoma showing both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining | |||
File:Chromogenic_immunohistochemistry.jpg|Chromogenic immunohistochemistry | |||
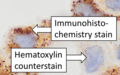
File:Immunohistochemistry_stain_versus_counterstain.png|Immunohistochemistry stain versus counterstain | |||
File:Positive_and_negative_controls_in_immunohistochemistry.png|Positive and negative controls in immunohistochemistry | |||
File:Kidney_cd10_ihc.jpg|Kidney CD10 IHC | |||
File:PIN-4_staining_of_benign_prostate_gland_and_adenocarcinoma.jpg|PIN-4 staining of benign prostate gland and adenocarcinoma | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:43, 18 February 2025
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a method in pathology that uses the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. This technique is widely used in the diagnosis of cancer, as it can demonstrate the presence and localization of specific proteins in tissues.
History[edit]
Immunohistochemistry was first described by Albert H. Coons in 1941 when he used a fluorescent tag to directly label antibodies to visualize pneumococcal antigens in infected tissues.
Methodology[edit]
The process of immunohistochemistry involves several steps. First, the tissue is fixed and embedded in paraffin to preserve the structure and proteins. The tissue is then sectioned and placed on a slide. The slide is then treated with antibodies that bind to the protein of interest. These antibodies can be visualized by a variety of methods, including fluorescence or enzymatic methods.
Applications[edit]
Immunohistochemistry is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Cancer diagnosis: IHC can be used to identify the type and origin of cancer cells.
- Infectious disease diagnosis: IHC can be used to identify specific pathogens in tissue samples.
- Research: IHC is used in research to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and protein expression in different tissues.
Limitations[edit]
While immunohistochemistry is a powerful tool, it does have some limitations. These include potential issues with specificity and sensitivity, as well as the need for careful control experiments to ensure accurate interpretation of results.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
-
Main staining patterns on immunohistochemistry
-
HSP IF IgA
-
Immunohistochemistry for p16 in uterine papillary serous adenocarcinoma showing both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining
-
Chromogenic immunohistochemistry
-
Immunohistochemistry stain versus counterstain
-
Positive and negative controls in immunohistochemistry
-
Kidney CD10 IHC
-
PIN-4 staining of benign prostate gland and adenocarcinoma