Foramen secundum: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Foramen Secundum == | |||
[[File:Foramen_ovale.png|thumb|right|Diagram showing the foramen ovale in the fetal heart.]] | |||
The '''foramen secundum''' is an important structure in the developing [[heart]] of a [[fetus]]. It is part of the [[interatrial septum]], which separates the [[right atrium]] from the [[left atrium]]. The foramen secundum plays a crucial role in fetal circulation, allowing blood to bypass the non-functioning fetal [[lungs]]. | |||
The foramen secundum | |||
== | === Development === | ||
==Clinical Significance== | During fetal development, the [[septum primum]] forms first, creating a partial partition between the right and left atria. As the septum primum grows, it leaves a temporary opening called the [[ostium primum]]. As the septum primum continues to develop, the ostium primum closes, and a new opening, the foramen secundum, forms in the upper part of the septum primum. | ||
The foramen secundum ensures that blood can continue to flow from the right atrium to the left atrium, bypassing the lungs, which are not yet in use. This is essential for proper fetal circulation, as the [[placenta]] is responsible for oxygenating the blood. | |||
=== Closure === | |||
After birth, the foramen secundum, along with the [[foramen ovale]], typically closes as the newborn begins to breathe air and the lungs become functional. The increased pressure in the left atrium causes the septum primum to press against the [[septum secundum]], effectively sealing the foramen ovale and secundum. This closure forms the [[fossa ovalis]] in the adult heart. | |||
=== Clinical Significance === | |||
In some cases, the foramen secundum may not close properly, leading to a condition known as a [[patent foramen ovale]] (PFO). A PFO can allow blood to flow between the atria, which may lead to complications such as [[stroke]] or [[migraine]]s in some individuals. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Foramen ovale]] | * [[Foramen ovale]] | ||
* [[Interatrial septum]] | |||
* [[Fetal circulation]] | * [[Fetal circulation]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Patent foramen ovale]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Cardiovascular system]] | ||
[[Category:Embryology]] | [[Category:Embryology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:33, 15 February 2025
Foramen Secundum[edit]
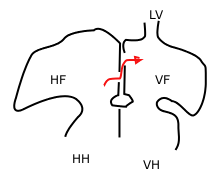
The foramen secundum is an important structure in the developing heart of a fetus. It is part of the interatrial septum, which separates the right atrium from the left atrium. The foramen secundum plays a crucial role in fetal circulation, allowing blood to bypass the non-functioning fetal lungs.
Development[edit]
During fetal development, the septum primum forms first, creating a partial partition between the right and left atria. As the septum primum grows, it leaves a temporary opening called the ostium primum. As the septum primum continues to develop, the ostium primum closes, and a new opening, the foramen secundum, forms in the upper part of the septum primum.
The foramen secundum ensures that blood can continue to flow from the right atrium to the left atrium, bypassing the lungs, which are not yet in use. This is essential for proper fetal circulation, as the placenta is responsible for oxygenating the blood.
Closure[edit]
After birth, the foramen secundum, along with the foramen ovale, typically closes as the newborn begins to breathe air and the lungs become functional. The increased pressure in the left atrium causes the septum primum to press against the septum secundum, effectively sealing the foramen ovale and secundum. This closure forms the fossa ovalis in the adult heart.
Clinical Significance[edit]
In some cases, the foramen secundum may not close properly, leading to a condition known as a patent foramen ovale (PFO). A PFO can allow blood to flow between the atria, which may lead to complications such as stroke or migraines in some individuals.