Hypoxia (medicine): Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
Hypoxia | | name = Hypoxia | ||
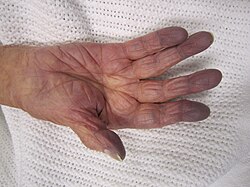
| image = [[File:Cynosis.JPG|250px]] | |||
| caption = Cyanosis, a common sign of hypoxia | |||
| field = [[Pulmonology]], [[Cardiology]] | |||
| synonyms = Oxygen deficiency | |||
| symptoms = [[Cyanosis]], [[confusion]], [[tachycardia]], [[shortness of breath]] | |||
| complications = [[Brain damage]], [[organ failure]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| causes = [[High altitude]], [[respiratory disease]], [[cardiac arrest]], [[anemia]], [[carbon monoxide poisoning]] | |||
| risks = [[Smoking]], [[chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]] (COPD), [[heart disease]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Arterial blood gas]], [[pulse oximetry]] | |||
| differential = [[Anemia]], [[cyanide poisoning]], [[methemoglobinemia]] | |||
| prevention = Avoidance of high altitudes, smoking cessation, management of underlying conditions | |||
| treatment = [[Oxygen therapy]], [[mechanical ventilation]], treatment of underlying cause | |||
| prognosis = Depends on cause and severity | |||
| frequency = Common in [[high altitude]] areas, patients with [[chronic lung disease]] | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|A condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply.}} | |||
==Hypoxia (medicine)== | |||
[[File:Ischemia.JPG|left|thumb|Ischemia can lead to hypoxia by restricting blood flow.]] | |||
Hypoxia in medicine refers to a condition where there is a deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues. It is a critical condition that can lead to severe consequences if not addressed promptly. Hypoxia can occur in various forms and can affect different parts of the body. | |||
==Types of Hypoxia== | ==Types of Hypoxia== | ||
Hypoxia can be classified into several types based on its cause and the mechanism by which it occurs: | |||
* '''[[Hypoxic hypoxia]]''': This occurs when there is a low partial pressure of oxygen in the air, leading to insufficient oxygen in the blood. It is commonly seen at high altitudes. | |||
Hypoxic hypoxia | * '''[[Anemic hypoxia]]''': This type occurs when the blood's capacity to carry oxygen is reduced, often due to a decrease in hemoglobin or red blood cells. | ||
* '''[[Stagnant hypoxia]]''': Also known as circulatory hypoxia, it occurs when there is inadequate blood flow to the tissues, as seen in conditions like [[ischemia]]. | |||
* '''[[Histotoxic hypoxia]]''': This occurs when the cells are unable to use the oxygen available to them, often due to toxins or poisons that interfere with cellular respiration. | |||
[[Anemic | ==Causes of Hypoxia== | ||
Hypoxia can result from a variety of causes, including: | |||
* [[Respiratory diseases]] such as [[chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]] (COPD) or [[asthma]]. | |||
[[Stagnant | * [[Cardiovascular diseases]] that impair blood flow, such as [[heart failure]] or [[ischemia]]. | ||
* Environmental factors like high altitude or carbon monoxide poisoning. | |||
* Anemia or other blood disorders that reduce oxygen-carrying capacity. | |||
[[Histotoxic | ==Symptoms of Hypoxia== | ||
The symptoms of hypoxia can vary depending on the severity and duration of the condition. Common symptoms include: | |||
==Symptoms== | * Shortness of breath | ||
The symptoms of hypoxia | * Rapid breathing | ||
* Confusion or cognitive impairment | |||
== | * Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin) | ||
* Tachycardia (rapid heart rate) | |||
==Diagnosis== | |||
Diagnosing hypoxia involves assessing the patient's symptoms, medical history, and conducting various tests. Common diagnostic tools include: | |||
* [[Pulse oximetry]] to measure blood oxygen levels. | |||
* [[Arterial blood gas]] analysis to assess oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood. | |||
* Imaging studies such as [[chest X-ray]] or [[CT scan]] to identify underlying causes. | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The treatment of hypoxia depends on its underlying cause. General approaches include: | |||
* Administering supplemental oxygen to increase blood oxygen levels. | |||
==See | * Treating the underlying condition, such as using bronchodilators for asthma or medications for heart failure. | ||
* [[ | * In severe cases, mechanical ventilation may be required to support breathing. | ||
* [[Respiratory | ==Prevention== | ||
* [[ | Preventing hypoxia involves managing risk factors and underlying conditions. Strategies include: | ||
* Avoiding high altitudes or using supplemental oxygen when necessary. | |||
* Managing chronic diseases like COPD or heart disease effectively. | |||
* Avoiding exposure to toxins and pollutants that can impair oxygen delivery. | |||
==See also== | |||
[[Category:Medical | * [[Ischemia]] | ||
[[Category:Respiratory | * [[Anemia]] | ||
* [[Respiratory failure]] | |||
* [[Oxygen therapy]] | |||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Respiratory diseases]] | |||
Latest revision as of 04:11, 7 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hypoxia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Oxygen deficiency |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Cyanosis, confusion, tachycardia, shortness of breath |
| Complications | Brain damage, organ failure |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | High altitude, respiratory disease, cardiac arrest, anemia, carbon monoxide poisoning |
| Risks | Smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart disease |
| Diagnosis | Arterial blood gas, pulse oximetry |
| Differential diagnosis | Anemia, cyanide poisoning, methemoglobinemia |
| Prevention | Avoidance of high altitudes, smoking cessation, management of underlying conditions |
| Treatment | Oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, treatment of underlying cause |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on cause and severity |
| Frequency | Common in high altitude areas, patients with chronic lung disease |
| Deaths | N/A |
A condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply.
Hypoxia (medicine)[edit]

Hypoxia in medicine refers to a condition where there is a deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues. It is a critical condition that can lead to severe consequences if not addressed promptly. Hypoxia can occur in various forms and can affect different parts of the body.
Types of Hypoxia[edit]
Hypoxia can be classified into several types based on its cause and the mechanism by which it occurs:
- Hypoxic hypoxia: This occurs when there is a low partial pressure of oxygen in the air, leading to insufficient oxygen in the blood. It is commonly seen at high altitudes.
- Anemic hypoxia: This type occurs when the blood's capacity to carry oxygen is reduced, often due to a decrease in hemoglobin or red blood cells.
- Stagnant hypoxia: Also known as circulatory hypoxia, it occurs when there is inadequate blood flow to the tissues, as seen in conditions like ischemia.
- Histotoxic hypoxia: This occurs when the cells are unable to use the oxygen available to them, often due to toxins or poisons that interfere with cellular respiration.
Causes of Hypoxia[edit]
Hypoxia can result from a variety of causes, including:
- Respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma.
- Cardiovascular diseases that impair blood flow, such as heart failure or ischemia.
- Environmental factors like high altitude or carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Anemia or other blood disorders that reduce oxygen-carrying capacity.
Symptoms of Hypoxia[edit]
The symptoms of hypoxia can vary depending on the severity and duration of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion or cognitive impairment
- Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin)
- Tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosing hypoxia involves assessing the patient's symptoms, medical history, and conducting various tests. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Pulse oximetry to measure blood oxygen levels.
- Arterial blood gas analysis to assess oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
- Imaging studies such as chest X-ray or CT scan to identify underlying causes.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of hypoxia depends on its underlying cause. General approaches include:
- Administering supplemental oxygen to increase blood oxygen levels.
- Treating the underlying condition, such as using bronchodilators for asthma or medications for heart failure.
- In severe cases, mechanical ventilation may be required to support breathing.
Prevention[edit]
Preventing hypoxia involves managing risk factors and underlying conditions. Strategies include:
- Avoiding high altitudes or using supplemental oxygen when necessary.
- Managing chronic diseases like COPD or heart disease effectively.
- Avoiding exposure to toxins and pollutants that can impair oxygen delivery.