Butaperazine: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Butaperazine''' is a | {{Short description|Overview of the antipsychotic medication Butaperazine}} | ||
==Butaperazine== | |||
[[File:Butaperazine_synthesis.svg|thumb|right|Chemical synthesis of Butaperazine]] | |||
'''Butaperazine''' is a typical antipsychotic medication belonging to the [[phenothiazine]] class. It is primarily used in the treatment of [[schizophrenia]] and other psychotic disorders. Butaperazine functions by blocking [[dopamine]] receptors in the brain, which helps to reduce symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions. | |||
==Pharmacology== | ==Pharmacology== | ||
Butaperazine acts | Butaperazine acts as a [[dopamine receptor antagonist]], particularly targeting the D2 receptors. This action is believed to be responsible for its antipsychotic effects. By inhibiting dopamine activity, Butaperazine can help to balance neurotransmitter levels in the brain, which is often disrupted in individuals with psychotic disorders. | ||
== | ==Chemical Structure== | ||
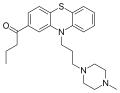
Butaperazine is | Butaperazine is a member of the phenothiazine class, which is characterized by a three-ring structure. The chemical synthesis of Butaperazine involves several steps, as illustrated in the accompanying diagram. The synthesis process is crucial for understanding the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drug. | ||
==Side Effects== | ==Side Effects== | ||
Common side effects of Butaperazine include [[sedation]], [[dry mouth]], [[constipation]], and [[blurred vision]]. More serious side effects can include [[extrapyramidal symptoms]] such as [[tardive dyskinesia]], which involves involuntary movements. Patients may also experience [[orthostatic hypotension]], which is a drop in blood pressure upon standing. | |||
== | ==Usage== | ||
Butaperazine is | Butaperazine is typically administered orally in tablet form. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the condition and the patient's response to the medication. It is important for patients to follow their healthcare provider's instructions and to report any adverse effects. | ||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Antipsychotic]] | |||
* [[Phenothiazine]] | * [[Phenothiazine]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Dopamine receptor antagonist]] | ||
* [[Schizophrenia]] | * [[Schizophrenia]] | ||
[[Category:Antipsychotics]] | |||
[[Category:Phenothiazines]] | [[Category:Phenothiazines]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Butaperazine.svg|Chemical structure of Butaperazine | |||
File:Butaperazine_synthesis.svg|Synthesis pathway of Butaperazine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:56, 17 February 2025
Overview of the antipsychotic medication Butaperazine
Butaperazine[edit]

Butaperazine is a typical antipsychotic medication belonging to the phenothiazine class. It is primarily used in the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. Butaperazine functions by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, which helps to reduce symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions.
Pharmacology[edit]
Butaperazine acts as a dopamine receptor antagonist, particularly targeting the D2 receptors. This action is believed to be responsible for its antipsychotic effects. By inhibiting dopamine activity, Butaperazine can help to balance neurotransmitter levels in the brain, which is often disrupted in individuals with psychotic disorders.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Butaperazine is a member of the phenothiazine class, which is characterized by a three-ring structure. The chemical synthesis of Butaperazine involves several steps, as illustrated in the accompanying diagram. The synthesis process is crucial for understanding the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drug.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of Butaperazine include sedation, dry mouth, constipation, and blurred vision. More serious side effects can include extrapyramidal symptoms such as tardive dyskinesia, which involves involuntary movements. Patients may also experience orthostatic hypotension, which is a drop in blood pressure upon standing.
Usage[edit]
Butaperazine is typically administered orally in tablet form. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the condition and the patient's response to the medication. It is important for patients to follow their healthcare provider's instructions and to report any adverse effects.
Related pages[edit]
-
Chemical structure of Butaperazine
-
Synthesis pathway of Butaperazine