Superior vena cava syndrome: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Superior vena cava syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:SVCcombo.JPG|250px]] | |||
| caption = CT scan showing superior vena cava syndrome | |||
| field = [[Cardiology]], [[Oncology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Swelling]] of face, neck, and upper limbs, [[dyspnea]], [[cough]], [[chest pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Cerebral edema]], [[airway obstruction]] | |||
| onset = Gradual or sudden | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| causes = [[Malignancy]] (e.g., [[lung cancer]], [[lymphoma]]), [[thrombosis]], [[infection]] | |||
| risks = [[Smoking]], [[central venous catheter]] placement | |||
| diagnosis = [[CT scan]], [[MRI]], [[venography]] | |||
| differential = [[Heart failure]], [[pericardial effusion]], [[tracheal compression]] | |||
| treatment = [[Radiation therapy]], [[chemotherapy]], [[stenting]], [[corticosteroids]] | |||
| prognosis = Depends on underlying cause | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
== Superior Vena Cava Syndrome == | == Superior Vena Cava Syndrome == | ||
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (SVCS) is a significant medical condition characterized by the obstruction of blood flow in the superior vena cava. This obstruction is typically caused by factors such as a [[malignant neoplasm]], [[thrombosis]], or an [[aneurysm]]. SVCS is considered a medical emergency and necessitates immediate treatment due to the critical role of the superior vena cava in returning deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart. | Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (SVCS) is a significant medical condition characterized by the obstruction of blood flow in the superior vena cava. This obstruction is typically caused by factors such as a [[malignant neoplasm]], [[thrombosis]], or an [[aneurysm]]. SVCS is considered a medical emergency and necessitates immediate treatment due to the critical role of the superior vena cava in returning deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart. | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/Mwu1dG9LfO4 | movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/Mwu1dG9LfO4 | ||
&rel=1 | &rel=1 | ||
| Line 13: | Line 29: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== Signs and Symptoms == | == Signs and Symptoms == | ||
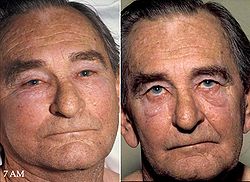
The clinical manifestations of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome include: | The clinical manifestations of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome include: | ||
* Swelling of the face, neck, and upper arms | * Swelling of the face, neck, and upper arms | ||
* Cyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the skin, particularly evident in the aforementioned areas | * Cyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the skin, particularly evident in the aforementioned areas | ||
| Line 22: | Line 36: | ||
* Orthopnea, difficulty in breathing that is experienced while lying flat | * Orthopnea, difficulty in breathing that is experienced while lying flat | ||
* Severe [[headache]] | * Severe [[headache]] | ||
These symptoms result from the increased venous pressure and reduced blood return to the heart. | These symptoms result from the increased venous pressure and reduced blood return to the heart. | ||
[[File:Superior.vena.cava.syndrome.aak.jpg|left|thumb|Symptoms of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome]] | |||
[[File:Superior.vena.cava.syndrome.aak.jpg|thumb | |||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The primary causes of SVCS include: | The primary causes of SVCS include: | ||
* '''Malignant Neoplasm''': Tumors, particularly lung cancer or lymphoma, can compress or invade the superior vena cava. | * '''Malignant Neoplasm''': Tumors, particularly lung cancer or lymphoma, can compress or invade the superior vena cava. | ||
* '''Thrombosis''': Blood clots within the vein can lead to obstruction. | * '''Thrombosis''': Blood clots within the vein can lead to obstruction. | ||
* '''Aneurysm''': An abnormal bulge in the wall of the vein can impede blood flow. | * '''Aneurysm''': An abnormal bulge in the wall of the vein can impede blood flow. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of SVCS involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Commonly employed imaging techniques include: | Diagnosis of SVCS involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Commonly employed imaging techniques include: | ||
* [[Chest X-ray]] | * [[Chest X-ray]] | ||
* [[CT scan]] | * [[CT scan]] | ||
* [[MRI]] | * [[MRI]] | ||
* [[Ultrasound]] | * [[Ultrasound]] | ||
These imaging modalities help in identifying the location and cause of the obstruction. | These imaging modalities help in identifying the location and cause of the obstruction. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment of SVCS aims at relieving the symptoms and addressing the underlying cause. Therapeutic approaches include: | Treatment of SVCS aims at relieving the symptoms and addressing the underlying cause. Therapeutic approaches include: | ||
* [[Chemotherapy]] and [[radiation therapy]] for cancer-related SVCS. | * [[Chemotherapy]] and [[radiation therapy]] for cancer-related SVCS. | ||
* Anticoagulation therapy for thrombosis. | * Anticoagulation therapy for thrombosis. | ||
* Surgical interventions in certain cases, such as stent placement. | * Surgical interventions in certain cases, such as stent placement. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Vena Cava]] | * [[Vena Cava]] | ||
* [[Oncology]] | * [[Oncology]] | ||
* [[Cardiology]] | * [[Cardiology]] | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
* [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/superior-vena-cava-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20350580 Mayo Clinic: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome] | * [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/superior-vena-cava-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20350580 Mayo Clinic: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome] | ||
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430940/ National Center for Biotechnology Information: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome] | * [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430940/ National Center for Biotechnology Information: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
[[Category:Oncology]] | [[Category:Oncology]] | ||
[[Category:Vascular Diseases]] | [[Category:Vascular Diseases]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:17, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Superior vena cava syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Swelling of face, neck, and upper limbs, dyspnea, cough, chest pain |
| Complications | Cerebral edema, airway obstruction |
| Onset | Gradual or sudden |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Malignancy (e.g., lung cancer, lymphoma), thrombosis, infection |
| Risks | Smoking, central venous catheter placement |
| Diagnosis | CT scan, MRI, venography |
| Differential diagnosis | Heart failure, pericardial effusion, tracheal compression |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stenting, corticosteroids |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome[edit]
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (SVCS) is a significant medical condition characterized by the obstruction of blood flow in the superior vena cava. This obstruction is typically caused by factors such as a malignant neoplasm, thrombosis, or an aneurysm. SVCS is considered a medical emergency and necessitates immediate treatment due to the critical role of the superior vena cava in returning deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart.
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
The clinical manifestations of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome include:
- Swelling of the face, neck, and upper arms
- Cyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the skin, particularly evident in the aforementioned areas
- Persistent cough
- Orthopnea, difficulty in breathing that is experienced while lying flat
- Severe headache
These symptoms result from the increased venous pressure and reduced blood return to the heart.

Causes[edit]
The primary causes of SVCS include:
- Malignant Neoplasm: Tumors, particularly lung cancer or lymphoma, can compress or invade the superior vena cava.
- Thrombosis: Blood clots within the vein can lead to obstruction.
- Aneurysm: An abnormal bulge in the wall of the vein can impede blood flow.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of SVCS involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Commonly employed imaging techniques include:
These imaging modalities help in identifying the location and cause of the obstruction.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of SVCS aims at relieving the symptoms and addressing the underlying cause. Therapeutic approaches include:
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer-related SVCS.
- Anticoagulation therapy for thrombosis.
- Surgical interventions in certain cases, such as stent placement.
See Also[edit]
External Links[edit]
- Mayo Clinic: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
References[edit]
<references/>


