Renal tubular acidosis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Renal tubular acidosis | |||
| image = [[File:Nephrocalcinosis.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Nephrocalcinosis, a possible complication of renal tubular acidosis | |||
| field = [[Nephrology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Fatigue]], [[muscle weakness]], [[polyuria]], [[polydipsia]], [[growth retardation]] in children | |||
| complications = [[Nephrocalcinosis]], [[kidney stones]], [[chronic kidney disease]] | |||
| onset = Variable, depending on type | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| types = [[Type 1 RTA|Type 1]], [[Type 2 RTA|Type 2]], [[Type 3 RTA|Type 3]], [[Type 4 RTA|Type 4]] | |||
| causes = Genetic mutations, autoimmune diseases, medications | |||
| risks = Family history, certain autoimmune disorders | |||
| diagnosis = [[Blood test|Blood tests]], [[urinalysis]], [[urine pH]] | |||
| differential = [[Metabolic acidosis]], [[chronic kidney disease]], [[Bartter syndrome]], [[Gitelman syndrome]] | |||
| treatment = [[Bicarbonate]] supplements, [[potassium]] supplements, dietary modifications | |||
| medication = [[Sodium bicarbonate]], [[potassium citrate]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depending on type and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:XrayRicketsLegssmall.jpg|X-ray of Rickets|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Aldosterone-2D-skeletal.svg|Aldosterone Structure|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Renal tubular acidosis''' ('''RTA''') is a medical condition that involves an accumulation of acid in the body due to a failure of the kidneys to appropriately acidify the urine. When the body performs normal metabolic processes, it produces acid. If this acid is not removed or neutralized, the blood will become too acidic. This can lead to electrolyte and fluid imbalances, which can cause symptoms and complications. | '''Renal tubular acidosis''' ('''RTA''') is a medical condition that involves an accumulation of acid in the body due to a failure of the kidneys to appropriately acidify the urine. When the body performs normal metabolic processes, it produces acid. If this acid is not removed or neutralized, the blood will become too acidic. This can lead to electrolyte and fluid imbalances, which can cause symptoms and complications. | ||
==Types== | ==Types== | ||
There are three main types of RTA, each with different causes and treatments. These are: | There are three main types of RTA, each with different causes and treatments. These are: | ||
* '''[[Type 1 RTA]]''' (or '''distal RTA'''): This type is caused by a failure of the acid secretion by the alpha intercalated cells of the cortical collecting duct of the distal nephron. This can be due to a variety of causes, including genetic mutations and autoimmune diseases. | * '''[[Type 1 RTA]]''' (or '''distal RTA'''): This type is caused by a failure of the acid secretion by the alpha intercalated cells of the cortical collecting duct of the distal nephron. This can be due to a variety of causes, including genetic mutations and autoimmune diseases. | ||
* '''[[Type 2 RTA]]''' (or '''proximal RTA'''): This type is caused by a failure of the proximal tubular cells to reabsorb filtered bicarbonate from the urine, leading to excessive bicarbonate loss. This can be due to genetic disorders, kidney diseases, or certain medications. | * '''[[Type 2 RTA]]''' (or '''proximal RTA'''): This type is caused by a failure of the proximal tubular cells to reabsorb filtered bicarbonate from the urine, leading to excessive bicarbonate loss. This can be due to genetic disorders, kidney diseases, or certain medications. | ||
* '''[[Type 4 RTA]]''' (or '''hyperkalemic RTA'''): This type is caused by a failure of the kidneys to excrete potassium, leading to hyperkalemia (high blood potassium levels). This can be due to adrenal gland disorders, certain medications, or chronic kidney disease. | * '''[[Type 4 RTA]]''' (or '''hyperkalemic RTA'''): This type is caused by a failure of the kidneys to excrete potassium, leading to hyperkalemia (high blood potassium levels). This can be due to adrenal gland disorders, certain medications, or chronic kidney disease. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of RTA can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms can include: | The symptoms of RTA can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms can include: | ||
* Fatigue | * Fatigue | ||
* Muscle weakness | * Muscle weakness | ||
| Line 19: | Line 35: | ||
* Increased thirst | * Increased thirst | ||
* Confusion or decreased alertness | * Confusion or decreased alertness | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The diagnosis of RTA is typically made based on the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests. These tests can include blood tests, urine tests, and sometimes genetic testing. | The diagnosis of RTA is typically made based on the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests. These tests can include blood tests, urine tests, and sometimes genetic testing. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The treatment of RTA typically involves correcting the acid-base imbalance with alkali therapy, treating the underlying cause of the condition, and managing any complications. | The treatment of RTA typically involves correcting the acid-base imbalance with alkali therapy, treating the underlying cause of the condition, and managing any complications. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Kidney disease]] | * [[Kidney disease]] | ||
* [[Metabolic acidosis]] | * [[Metabolic acidosis]] | ||
* [[Acid-base homeostasis]] | * [[Acid-base homeostasis]] | ||
[[Category:Kidney diseases]] | [[Category:Kidney diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Acid–base disturbances]] | [[Category:Acid–base disturbances]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:59, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Renal tubular acidosis | |
|---|---|
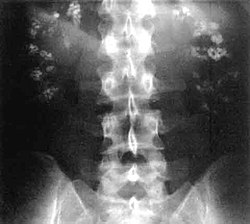
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, muscle weakness, polyuria, polydipsia, growth retardation in children |
| Complications | Nephrocalcinosis, kidney stones, chronic kidney disease |
| Onset | Variable, depending on type |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, Type 4 |
| Causes | Genetic mutations, autoimmune diseases, medications |
| Risks | Family history, certain autoimmune disorders |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests, urinalysis, urine pH |
| Differential diagnosis | Metabolic acidosis, chronic kidney disease, Bartter syndrome, Gitelman syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Bicarbonate supplements, potassium supplements, dietary modifications |
| Medication | Sodium bicarbonate, potassium citrate |
| Prognosis | Variable, depending on type and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |


Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a medical condition that involves an accumulation of acid in the body due to a failure of the kidneys to appropriately acidify the urine. When the body performs normal metabolic processes, it produces acid. If this acid is not removed or neutralized, the blood will become too acidic. This can lead to electrolyte and fluid imbalances, which can cause symptoms and complications.
Types[edit]
There are three main types of RTA, each with different causes and treatments. These are:
- Type 1 RTA (or distal RTA): This type is caused by a failure of the acid secretion by the alpha intercalated cells of the cortical collecting duct of the distal nephron. This can be due to a variety of causes, including genetic mutations and autoimmune diseases.
- Type 2 RTA (or proximal RTA): This type is caused by a failure of the proximal tubular cells to reabsorb filtered bicarbonate from the urine, leading to excessive bicarbonate loss. This can be due to genetic disorders, kidney diseases, or certain medications.
- Type 4 RTA (or hyperkalemic RTA): This type is caused by a failure of the kidneys to excrete potassium, leading to hyperkalemia (high blood potassium levels). This can be due to adrenal gland disorders, certain medications, or chronic kidney disease.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of RTA can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms can include:
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Confusion or decreased alertness
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of RTA is typically made based on the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests. These tests can include blood tests, urine tests, and sometimes genetic testing.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of RTA typically involves correcting the acid-base imbalance with alkali therapy, treating the underlying cause of the condition, and managing any complications.


