Linitis plastica: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Linitis plastica | |||
| image = [[File:Linitis_plastica.jpg]] | |||
| caption = Endoscopic image of linitis plastica | |||
| field = [[Gastroenterology]], [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = Leather bottle stomach | |||
| symptoms = [[Weight loss]], [[abdominal pain]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[early satiety]] | |||
| complications = [[Metastasis]], [[malnutrition]] | |||
| onset = Typically in [[adulthood]] | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = [[Diffuse gastric cancer]], [[infiltrative carcinoma]] | |||
| risks = [[Helicobacter pylori]] infection, [[genetic predisposition]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Endoscopy]], [[biopsy]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Peptic ulcer disease]], [[gastritis]], [[gastric lymphoma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[chemotherapy]], [[radiation therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Poor | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Infiltrative_gastric_cancer_showing_thickened_stomach_wall.jpg|Infiltrative gastric cancer showing thickened stomach wall|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Linitis_plastica_2.jpg|Linitis plastica|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Linitis plastica''' is a type of [[gastric cancer]] that causes the walls of the [[stomach]] to harden, reducing its elasticity. This condition is also known as "leather bottle stomach" due to the appearance and texture of the stomach walls. | '''Linitis plastica''' is a type of [[gastric cancer]] that causes the walls of the [[stomach]] to harden, reducing its elasticity. This condition is also known as "leather bottle stomach" due to the appearance and texture of the stomach walls. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The symptoms of linitis plastica can be non-specific and may be similar to other [[gastrointestinal disorders]]. These can include: | The symptoms of linitis plastica can be non-specific and may be similar to other [[gastrointestinal disorders]]. These can include: | ||
| Line 8: | Line 28: | ||
* [[Anorexia (symptom)|Loss of appetite]] | * [[Anorexia (symptom)|Loss of appetite]] | ||
* [[Dysphagia|Difficulty swallowing]] | * [[Dysphagia|Difficulty swallowing]] | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The exact cause of linitis plastica is unknown, but it is believed to be associated with certain risk factors such as [[Helicobacter pylori|H. pylori infection]], [[gastritis]], and [[pernicious anemia]]. | The exact cause of linitis plastica is unknown, but it is believed to be associated with certain risk factors such as [[Helicobacter pylori|H. pylori infection]], [[gastritis]], and [[pernicious anemia]]. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of linitis plastica can be challenging due to its non-specific symptoms. It often involves a combination of [[medical history]], physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as [[endoscopy]], [[biopsy]], and [[imaging studies]]. | Diagnosis of linitis plastica can be challenging due to its non-specific symptoms. It often involves a combination of [[medical history]], physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as [[endoscopy]], [[biopsy]], and [[imaging studies]]. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for linitis plastica typically involves [[surgery]], [[chemotherapy]], and [[radiation therapy]]. The choice of treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the patient's overall health, and their personal preferences. | Treatment for linitis plastica typically involves [[surgery]], [[chemotherapy]], and [[radiation therapy]]. The choice of treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the patient's overall health, and their personal preferences. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for linitis plastica is generally poor, with a low survival rate. However, early detection and treatment can improve the prognosis. | The prognosis for linitis plastica is generally poor, with a low survival rate. However, early detection and treatment can improve the prognosis. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Gastric cancer]] | * [[Gastric cancer]] | ||
* [[Stomach]] | * [[Stomach]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal disorders]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Stomach disorders]] | [[Category:Stomach disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Cancer]] | [[Category:Cancer]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:16, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Linitis plastica | |
|---|---|
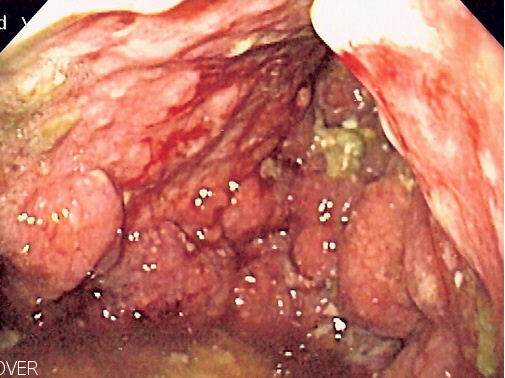
| |
| Synonyms | Leather bottle stomach |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Weight loss, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, early satiety |
| Complications | Metastasis, malnutrition |
| Onset | Typically in adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Diffuse gastric cancer, infiltrative carcinoma |
| Risks | Helicobacter pylori infection, genetic predisposition |
| Diagnosis | Endoscopy, biopsy, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Peptic ulcer disease, gastritis, gastric lymphoma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Poor |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |


Linitis plastica is a type of gastric cancer that causes the walls of the stomach to harden, reducing its elasticity. This condition is also known as "leather bottle stomach" due to the appearance and texture of the stomach walls.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of linitis plastica can be non-specific and may be similar to other gastrointestinal disorders. These can include:
Causes[edit]
The exact cause of linitis plastica is unknown, but it is believed to be associated with certain risk factors such as H. pylori infection, gastritis, and pernicious anemia.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of linitis plastica can be challenging due to its non-specific symptoms. It often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, biopsy, and imaging studies.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for linitis plastica typically involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. The choice of treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the patient's overall health, and their personal preferences.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for linitis plastica is generally poor, with a low survival rate. However, early detection and treatment can improve the prognosis.


