Spermatocytic tumor: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Spermatocytic tumor | |||
| image = [[File:Spermatocytic_seminoma_high_mag.jpg|alt=Micrograph of a spermatocytic tumor]] | |||
| caption = Micrograph of a spermatocytic tumor | |||
| field = [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = Spermatocytic seminoma | |||
| symptoms = Testicular mass | |||
| complications = Rarely [[metastasis]] | |||
| onset = Typically in older adults | |||
| duration = Indolent | |||
| types = | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = Age (older adults) | |||
| diagnosis = [[Histopathology]] | |||
| differential = [[Seminoma]], [[Embryonal carcinoma]], [[Lymphoma]] | |||
| prevention = | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]] | |||
| medication = | |||
| prognosis = Excellent with treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Spermatocytic_seminoma_intermed_mag.jpg|Spermatocytic tumor|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Spermatocytic tumor''' is a rare type of [[testicular tumor]] that is typically benign, meaning it does not usually spread to other parts of the body. It is also known as '''spermatocytic seminoma'''. | '''Spermatocytic tumor''' is a rare type of [[testicular tumor]] that is typically benign, meaning it does not usually spread to other parts of the body. It is also known as '''spermatocytic seminoma'''. | ||
== Introduction == | |||
== | |||
Spermatocytic tumors are a distinct type of [[seminoma]], which is a form of [[testicular cancer]]. Unlike typical seminomas, spermatocytic tumors are not associated with [[intratubular germ cell neoplasia]] and have a different tumor cell morphology. They are also not associated with [[isochromosome 12p]], which is a common genetic abnormality in other types of testicular germ cell tumors. | Spermatocytic tumors are a distinct type of [[seminoma]], which is a form of [[testicular cancer]]. Unlike typical seminomas, spermatocytic tumors are not associated with [[intratubular germ cell neoplasia]] and have a different tumor cell morphology. They are also not associated with [[isochromosome 12p]], which is a common genetic abnormality in other types of testicular germ cell tumors. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The most common symptom of a spermatocytic tumor is a painless swelling or lump in the [[testicle]]. Some men may also experience discomfort or a heavy feeling in the scrotum. | The most common symptom of a spermatocytic tumor is a painless swelling or lump in the [[testicle]]. Some men may also experience discomfort or a heavy feeling in the scrotum. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
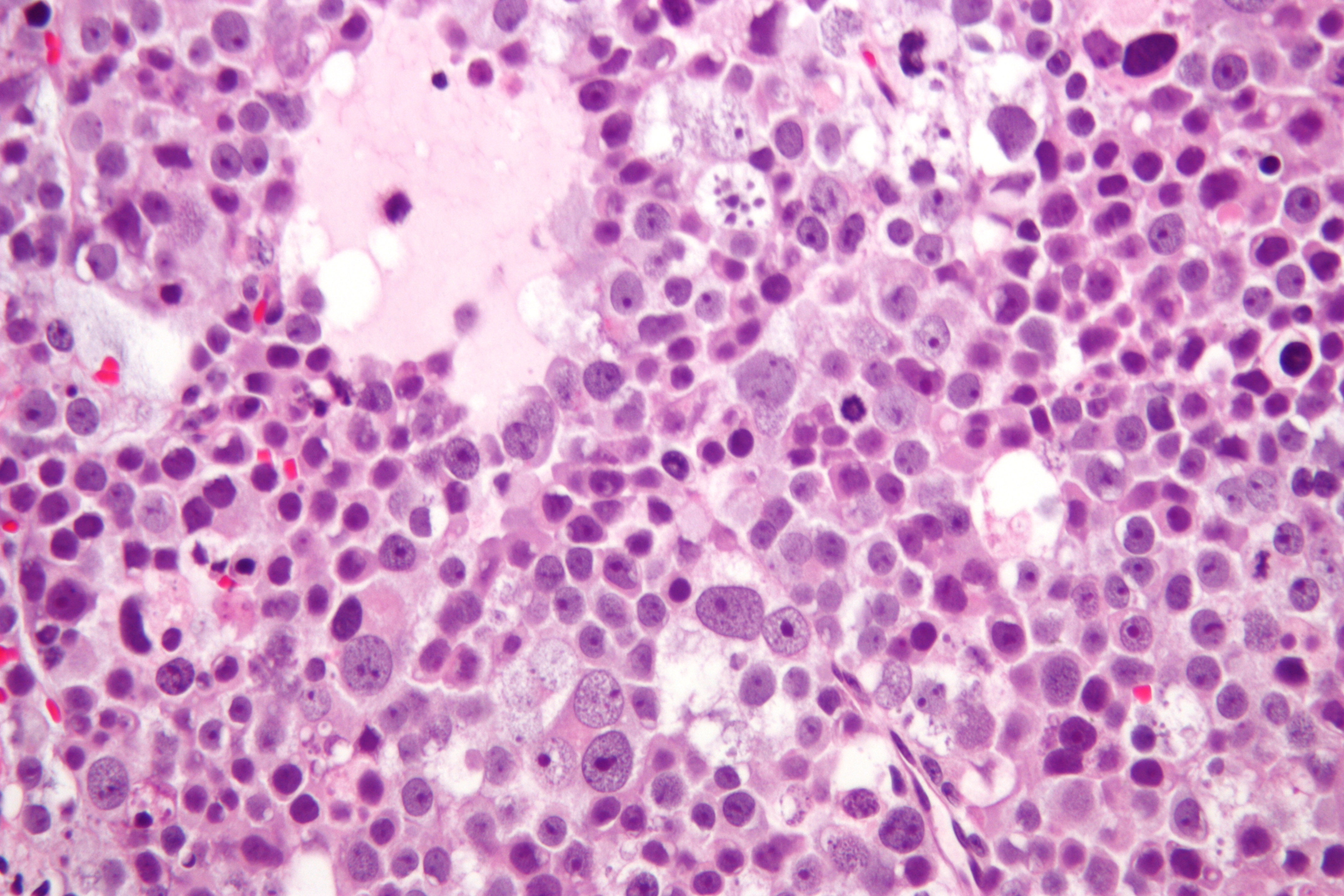
Diagnosis of a spermatocytic tumor is typically made through a combination of physical examination, [[ultrasound]] imaging, and [[biopsy]] of the testicular tissue. The tumor cells of a spermatocytic tumor have a distinct appearance under the microscope, which helps to differentiate them from other types of testicular tumors. | Diagnosis of a spermatocytic tumor is typically made through a combination of physical examination, [[ultrasound]] imaging, and [[biopsy]] of the testicular tissue. The tumor cells of a spermatocytic tumor have a distinct appearance under the microscope, which helps to differentiate them from other types of testicular tumors. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The primary treatment for a spermatocytic tumor is surgical removal of the affected testicle, a procedure known as [[orchiectomy]]. Because spermatocytic tumors are typically benign and do not spread to other parts of the body, additional treatment such as [[chemotherapy]] or [[radiation therapy]] is usually not necessary. | The primary treatment for a spermatocytic tumor is surgical removal of the affected testicle, a procedure known as [[orchiectomy]]. Because spermatocytic tumors are typically benign and do not spread to other parts of the body, additional treatment such as [[chemotherapy]] or [[radiation therapy]] is usually not necessary. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for men with a spermatocytic tumor is generally excellent. Because these tumors are typically benign and do not spread, the survival rate is nearly 100%. | The prognosis for men with a spermatocytic tumor is generally excellent. Because these tumors are typically benign and do not spread, the survival rate is nearly 100%. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Testicular cancer]] | * [[Testicular cancer]] | ||
* [[Seminoma]] | * [[Seminoma]] | ||
* [[Orchiectomy]] | * [[Orchiectomy]] | ||
[[Category:Testicular cancer]] | [[Category:Testicular cancer]] | ||
[[Category:Tumors]] | [[Category:Tumors]] | ||
[[Category:Urology]] | [[Category:Urology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:44, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Spermatocytic tumor | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Spermatocytic seminoma |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Testicular mass |
| Complications | Rarely metastasis |
| Onset | Typically in older adults |
| Duration | Indolent |
| Types | |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Age (older adults) |
| Diagnosis | Histopathology |
| Differential diagnosis | Seminoma, Embryonal carcinoma, Lymphoma |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Surgery |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Excellent with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Spermatocytic tumor is a rare type of testicular tumor that is typically benign, meaning it does not usually spread to other parts of the body. It is also known as spermatocytic seminoma.
Introduction[edit]
Spermatocytic tumors are a distinct type of seminoma, which is a form of testicular cancer. Unlike typical seminomas, spermatocytic tumors are not associated with intratubular germ cell neoplasia and have a different tumor cell morphology. They are also not associated with isochromosome 12p, which is a common genetic abnormality in other types of testicular germ cell tumors.
Symptoms[edit]
The most common symptom of a spermatocytic tumor is a painless swelling or lump in the testicle. Some men may also experience discomfort or a heavy feeling in the scrotum.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a spermatocytic tumor is typically made through a combination of physical examination, ultrasound imaging, and biopsy of the testicular tissue. The tumor cells of a spermatocytic tumor have a distinct appearance under the microscope, which helps to differentiate them from other types of testicular tumors.
Treatment[edit]
The primary treatment for a spermatocytic tumor is surgical removal of the affected testicle, a procedure known as orchiectomy. Because spermatocytic tumors are typically benign and do not spread to other parts of the body, additional treatment such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy is usually not necessary.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for men with a spermatocytic tumor is generally excellent. Because these tumors are typically benign and do not spread, the survival rate is nearly 100%.


