Ileus: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
== | | name = Ileus | ||
| image = [[File:Ileus2.png|left|thumb|250px|X-ray of a patient with ileus]] | |||
| caption = X-ray showing ileus | |||
| field = [[Gastroenterology]] | |||
| synonyms = [[Intestinal obstruction]] | |||
* [[ | | symptoms = [[Abdominal pain]], [[bloating]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[constipation]] | ||
* [[Electrolyte | | complications = [[Bowel perforation]], [[sepsis]] | ||
* [[ | | onset = Sudden or gradual | ||
| duration = Varies | |||
== Symptoms == | | causes = [[Surgery]], [[medications]], [[infections]], [[electrolyte imbalance]] | ||
The symptoms of ileus can vary, but | | risks = [[Abdominal surgery]], [[opioid use]], [[elderly age]] | ||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[X-ray]], [[CT scan]] | |||
* | | differential = [[Mechanical bowel obstruction]], [[gastroenteritis]], [[appendicitis]] | ||
* | | treatment = [[Bowel rest]], [[nasogastric tube]], [[IV fluids]], [[surgery]] | ||
* | | medication = [[Prokinetics]], [[analgesics]] | ||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in hospitalized patients | |||
}} | |||
== Diagnosis == | {{Short description|A medical condition characterized by a lack of movement in the intestines}} | ||
'''Ileus''' is a medical condition characterized by a lack of movement in the intestines, leading to a buildup of food material and gas. This can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation. Ileus can occur as a result of surgery, certain medications, or other medical conditions that affect the normal peristaltic movements of the intestines. | |||
==Causes== | |||
* [[ | Ileus can be caused by a variety of factors, including: | ||
* [[Postoperative ileus]]: This is a common form of ileus that occurs after abdominal surgery. The manipulation of the intestines during surgery can temporarily disrupt their normal function. | |||
* [[Blood tests]]: | * [[Medications]]: Certain medications, such as opioids, can slow down intestinal motility and lead to ileus. | ||
* [[Electrolyte imbalances]]: Imbalances in electrolytes such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium can affect muscle contractions in the intestines. | |||
== Treatment == | * [[Infections]]: Infections within the abdomen, such as [[peritonitis]], can lead to ileus. | ||
* [[Inflammatory conditions]]: Conditions like [[Crohn's disease]] or [[ulcerative colitis]] can cause inflammation that affects intestinal motility. | |||
==Symptoms== | |||
* [[ | The symptoms of ileus can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause, but commonly include: | ||
* [[ | * Abdominal pain and cramping | ||
* [[Surgery]]: In | * Bloating and distension | ||
* Nausea and vomiting | |||
== See also == | * Constipation or inability to pass gas | ||
==Diagnosis== | |||
Diagnosis of ileus typically involves a combination of: | |||
* [[Physical examination]]: A doctor may listen for bowel sounds and check for abdominal tenderness. | |||
* [[Imaging studies]]: [[X-rays]], [[CT scans]], or [[ultrasound]] may be used to visualize the intestines and identify any blockages or abnormalities. | |||
* [[Blood tests]]: These can help identify electrolyte imbalances or signs of infection. | |||
==Treatment== | |||
Treatment for ileus depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common approaches include: | |||
* [[Bowel rest]]: Patients may be advised to refrain from eating or drinking to allow the intestines to rest. | |||
* [[Nasogastric tube]]: A tube may be inserted through the nose into the stomach to relieve pressure and remove excess gas and fluids. | |||
* [[Medications]]: Prokinetic agents may be used to stimulate intestinal motility. | |||
* [[Surgery]]: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove any obstructions or correct underlying issues. | |||
==Prevention== | |||
Preventive measures for ileus include: | |||
* Minimizing the use of medications that can slow intestinal motility. | |||
* Encouraging early mobilization and ambulation after surgery. | |||
* Maintaining adequate hydration and electrolyte balance. | |||
==See also== | |||
* [[Bowel obstruction]] | |||
* [[Peristalsis]] | |||
* [[Gastrointestinal tract]] | * [[Gastrointestinal tract]] | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:43, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Ileus | |
|---|---|
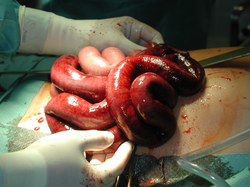 | |
| Synonyms | Intestinal obstruction |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, constipation |
| Complications | Bowel perforation, sepsis |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Surgery, medications, infections, electrolyte imbalance |
| Risks | Abdominal surgery, opioid use, elderly age |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray, CT scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Mechanical bowel obstruction, gastroenteritis, appendicitis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Bowel rest, nasogastric tube, IV fluids, surgery |
| Medication | Prokinetics, analgesics |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in hospitalized patients |
| Deaths | N/A |
A medical condition characterized by a lack of movement in the intestines
Ileus is a medical condition characterized by a lack of movement in the intestines, leading to a buildup of food material and gas. This can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation. Ileus can occur as a result of surgery, certain medications, or other medical conditions that affect the normal peristaltic movements of the intestines.
Causes[edit]
Ileus can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Postoperative ileus: This is a common form of ileus that occurs after abdominal surgery. The manipulation of the intestines during surgery can temporarily disrupt their normal function.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as opioids, can slow down intestinal motility and lead to ileus.
- Electrolyte imbalances: Imbalances in electrolytes such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium can affect muscle contractions in the intestines.
- Infections: Infections within the abdomen, such as peritonitis, can lead to ileus.
- Inflammatory conditions: Conditions like Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis can cause inflammation that affects intestinal motility.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of ileus can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause, but commonly include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Bloating and distension
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation or inability to pass gas
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of ileus typically involves a combination of:
- Physical examination: A doctor may listen for bowel sounds and check for abdominal tenderness.
- Imaging studies: X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasound may be used to visualize the intestines and identify any blockages or abnormalities.
- Blood tests: These can help identify electrolyte imbalances or signs of infection.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for ileus depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common approaches include:
- Bowel rest: Patients may be advised to refrain from eating or drinking to allow the intestines to rest.
- Nasogastric tube: A tube may be inserted through the nose into the stomach to relieve pressure and remove excess gas and fluids.
- Medications: Prokinetic agents may be used to stimulate intestinal motility.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove any obstructions or correct underlying issues.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures for ileus include:
- Minimizing the use of medications that can slow intestinal motility.
- Encouraging early mobilization and ambulation after surgery.
- Maintaining adequate hydration and electrolyte balance.