Bromodeoxyuridine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Bromodeoxyuridine.svg|Bromodeoxyuridine | File:Bromodeoxyuridine.svg|Bromodeoxyuridine | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:22, 16 March 2025
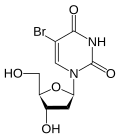
Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) is a synthetic nucleoside that is an analog of thymidine. It is commonly used in the detection of proliferating cells in living tissues. BrdU is incorporated into the newly synthesized DNA of replicating cells (during the S phase of the cell cycle), substituting for thymidine during DNA replication.
Structure and Function[edit]
BrdU is structurally similar to thymidine, with the exception that it contains a bromine atom in place of a methyl group. This small change allows BrdU to be incorporated into DNA in place of thymidine. Once incorporated, BrdU can be detected using specific antibodies, allowing researchers to identify cells that are actively dividing.
Applications in Research[edit]
BrdU is widely used in cell biology and molecular biology to study cell proliferation. It is particularly useful in the fields of oncology, neuroscience, and developmental biology. By administering BrdU to living organisms or cell cultures, researchers can label and track the proliferation of cells over time.
Oncology[edit]
In cancer research, BrdU is used to measure the growth rate of tumors. By determining the proportion of cells that are in the S phase, researchers can gain insights into the aggressiveness of a tumor and the effectiveness of anti-cancer treatments.
Neuroscience[edit]
In neuroscience, BrdU labeling is used to study neurogenesis, the process by which new neurons are formed in the brain. This is particularly important in understanding brain development and the potential for brain repair following injury.
Developmental Biology[edit]
In developmental biology, BrdU is used to study the patterns of cell division and differentiation during the development of organisms. This can provide valuable information about the mechanisms that control development and the formation of tissues and organs.
Detection Methods[edit]
The detection of BrdU incorporation is typically performed using immunohistochemistry or flow cytometry. In immunohistochemistry, tissue sections are treated with anti-BrdU antibodies, which bind specifically to BrdU. These antibodies are then visualized using various detection systems, such as fluorescent or chromogenic labels. In flow cytometry, cells are labeled with anti-BrdU antibodies and then analyzed to determine the proportion of cells that have incorporated BrdU.
Safety and Handling[edit]
BrdU is a mutagen and should be handled with care. Appropriate safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment and proper disposal methods, should be followed when working with BrdU.
Related Pages[edit]
- Thymidine
- Cell cycle
- DNA replication
- Immunohistochemistry
- Flow cytometry
- Neurogenesis
- Oncology
- Developmental biology
Categories[edit]
-
Bromodeoxyuridine