HOT-7: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{Psychoactive drug-stub}} | {{Psychoactive drug-stub}} | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
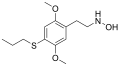
<gallery> | |||
File:HOT-7.svg|HOT-7 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:36, 3 March 2025
HOT-7 or 7-Hydroxy-alpha-methyltryptamine is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug that is used for its mind-altering effects. It is a member of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes.
History[edit]
HOT-7 was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, a renowned American medicinal chemist and psychopharmacologist. Shulgin is known for his work in the field of psychoactive drugs, particularly the synthesis and testing of new drugs.
Chemistry[edit]
HOT-7 is a derivative of the tryptamine chemical class, which is a group of compounds that are structurally similar to the amino acid tryptophan. It is specifically a derivative of alpha-methyltryptamine (AMT), with a hydroxy group added at the 7 position of the indole ring.
Effects[edit]
The effects of HOT-7 are similar to those of other psychedelic drugs, including alterations in thought, perception, and mood. Users may experience visual hallucinations, changes in perception of time, and heightened emotional sensitivity. The duration of effects is typically several hours.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of HOT-7 varies by country. In some countries, it is classified as a controlled substance, while in others it is legal to possess and use.
Health Risks[edit]
As with any psychedelic drug, use of HOT-7 carries potential health risks. These can include psychological distress, such as anxiety and paranoia, as well as physical risks such as increased heart rate and blood pressure.
See Also[edit]
This article is a Psychoactive drug-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
HOT-7