Bergapten: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Bergapten == | |||
<gallery> | |||
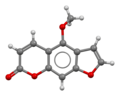
File:Bergapten-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png|Bergapten from crystal 3D ball-and-stick model | |||
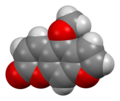
File:Bergapten-from-xtal-3D-sf.png|Bergapten from crystal 3D space-filling model | |||
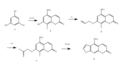
File:Condensed_version_of_efficient_synthesis_of_Bergapten.png|Condensed version of efficient synthesis of Bergapten | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:51, 27 February 2025
Bergapten is a psoralen (also known as furocoumarins) that is found in several plants, including Parsnips, Celery, and Figs. It is a potent photosensitizer and has been used in the treatment of Psoriasis and Vitiligo.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Bergapten is a linear furanocoumarin and is structurally related to other furocoumarins such as Psoralen and Methoxsalen. It has a molecular formula of C12H8O4 and a molecular weight of 216.19 g/mol.
Sources[edit]
Bergapten is found in a variety of plants, including the Apiaceae family (which includes parsnips and celery) and the Moraceae family (which includes figs). It is also found in the essential oils of Citrus fruits.
Medical Uses[edit]
Bergapten has been used in PUVA therapy, a type of ultraviolet light therapy for skin diseases. It is applied topically or taken orally, and then the skin is exposed to UVA light. This causes the bergapten to become activated and bind to the DNA of skin cells, slowing their growth.
Safety[edit]
Exposure to bergapten can cause Phytophotodermatitis, a skin reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with certain plants and is then exposed to sunlight. Symptoms can include redness, itching, and blisters.