Tetramethylurea: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[Category:Organic chemistry]] | [[Category:Organic chemistry]] | ||
[[Category:Ureas]] | [[Category:Ureas]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
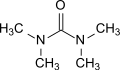
File:Tetramethylharnstoff_Struktur.svg|Tetramethylurea structure | |||
File:Tetramethylharnstoff_aus_Phosgen.svg|Synthesis of Tetramethylurea from phosgene | |||
File:Tetramethylharnstoff_aus_Diphenylcarbonat.svg|Synthesis of Tetramethylurea from diphenyl carbonate | |||
File:Oxidation_von_TDAE.svg|Oxidation of TDAE | |||
File:Polymerisation_von_p-Aminobenzoylchlorid.svg|Polymerization of p-Aminobenzoyl chloride | |||
File:2-tert.-Butyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethylguanidin.svg|2-tert-Butyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethylguanidine | |||
File:Uroniumsalz_mit_Acetobromglucose.svg|Uronium salt with acetobromglucose | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:33, 18 February 2025
Tetramethylurea (TMU) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)4N2O. It is a colorless liquid, soluble in water and common organic solvents. Tetramethylurea is used as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis.
Structure and Bonding[edit]
Tetramethylurea is a urea derivative and has a planar molecular geometry. The molecule is symmetric, with the nitrogen atoms forming a bridge between the two carbonyl groups. The carbonyl groups are in a trans configuration, which minimizes steric hindrance and allows for optimal overlap of the nitrogen's lone pair of electrons with the carbonyl group's antibonding orbital.
Synthesis[edit]
Tetramethylurea can be synthesized from dimethylamine and carbon dioxide. The reaction proceeds via the formation of a carbamate, which is then dehydrated to form the urea derivative.
Applications[edit]
Tetramethylurea is primarily used as a solvent in organic synthesis. It is particularly useful for reactions that require a polar, aprotic solvent. Additionally, it is used as a reagent in the synthesis of other organic compounds.
Safety[edit]
Like other urea derivatives, tetramethylurea is considered to be of low toxicity. However, it can cause irritation to the eyes and skin, and may be harmful if swallowed or inhaled.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
External Links[edit]
- PubChem entry for Tetramethylurea
- ChemSpider entry for Tetramethylurea
-
Tetramethylurea structure
-
Synthesis of Tetramethylurea from phosgene
-
Synthesis of Tetramethylurea from diphenyl carbonate
-
Oxidation of TDAE
-
Polymerization of p-Aminobenzoyl chloride
-
2-tert-Butyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethylguanidine
-
Uronium salt with acetobromglucose