Decalin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
== Decalin == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Decaline.png|Decalin | |||
File:Cis-trans_isomerism_of_decahydronaphthalene.svg|Cis-trans isomerism of decahydronaphthalene | |||
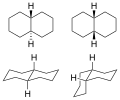
File:cis-decalin_double_chair.png|Cis-decalin double chair | |||
File:trans-decalin_double_chair.png|Trans-decalin double chair | |||
File:Cisdecalin_conformations.png|Cisdecalin conformations | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:01, 18 February 2025
Decalin (C10H18), also known as decahydronaphthalene, is a organic compound that consists of two fused cyclohexane rings. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature and is used in various industrial applications due to its chemical stability and nonpolar properties. Decalin exists in two forms: cis-decalin, where the hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the fused ring junction, and trans-decalin, where the hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides. The trans form is more stable due to less steric hindrance between hydrogen atoms.
Properties and Production[edit]
Decalin has a boiling point of approximately 187°C and a melting point that varies between the cis and trans forms; cis-decalin has a melting point of -43°C, while trans-decalin melts at -30°C. It is insoluble in water but soluble in many organic solvents such as ethanol, diethyl ether, and benzene.
Commercially, decalin is produced by hydrogenation of naphthalene, a process that involves the addition of hydrogen to naphthalene in the presence of a catalyst under high pressure and temperature.
Uses[edit]
Decalin is utilized in a variety of applications. It serves as a solvent in the paint and coatings industry, a dielectric fluid in electrical systems, and a component in heat transfer fluids. Additionally, its high boiling point and chemical stability make it suitable for use in high-temperature reactions as a solvent.
In the laboratory, decalin is often used as a solvent for the synthesis and study of various organic compounds. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of materials makes it valuable in research settings.
Health and Safety[edit]
Exposure to decalin can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. It is considered to have low acute toxicity, but long-term exposure can lead to respiratory issues, skin irritation, and other health problems. Safety measures include using decalin in well-ventilated areas, wearing protective clothing, and following proper storage and handling procedures to minimize exposure.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Decalin can have adverse effects on the environment if not handled properly. It is relatively persistent in the environment and can contaminate water and soil. Proper disposal and spill management are essential to prevent environmental contamination.
See Also[edit]
Decalin[edit]
-
Decalin
-
Cis-trans isomerism of decahydronaphthalene
-
Cis-decalin double chair
-
Trans-decalin double chair
-
Cisdecalin conformations