Ibogaine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Dissociatives]] | [[Category:Dissociatives]] | ||
[[Category:Indole alkaloids]] | [[Category:Indole alkaloids]] | ||
== Ibogaine == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ibogaine.svg|Ibogaine chemical structure | |||
File:Ibogaine-from-xtal-Mercury-3D-bs.png|3D model of Ibogaine from crystal structure | |||
File:Tabernanthe_iboga_bark_powder.jpg|Tabernanthe iboga bark powder | |||
File:Tryptamine_structure.png|Tryptamine structure | |||
File:Biosynthesis_of_ibogaine.jpg|Biosynthesis of Ibogaine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:49, 18 February 2025
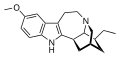
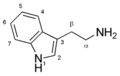
Ibogaine is a naturally occurring psychoactive substance found in various plants in the Apocynaceae family, such as Tabernanthe iboga, Voacanga africana, and Tabernaemontana undulata. It is a psychedelic with dissociative properties.
Chemistry[edit]
Ibogaine is an indole alkaloid, a class of naturally occurring compounds that are widely distributed in the plant kingdom. Ibogaine can be obtained either by extraction from the iboga plant or by semi-synthesis from the precursor compound voacangine, another plant alkaloid. The total synthesis of ibogaine was first described in 1956<ref>,
Total Synthesis of Ibogaine, Some Journal, 1956, Vol. ..(Issue: ..), pp. .., DOI: ..,</ref>.
The structure of ibogaine was elucidated by X-ray crystallography in 1960<ref>,
Structure Elucidation of Ibogaine by X-ray Crystallography, Crystallography Journal, 1960, Vol. ..(Issue: ..), pp. .., DOI: ..,</ref>.
Effects[edit]
Ibogaine is known for its psychedelic and dissociative effects. More research is required to fully understand these properties and their potential therapeutic applications.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of ibogaine varies greatly worldwide. In some jurisdictions, it is classified as a controlled substance due to its psychoactive properties.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />