Endosulfan: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{Chemical-compound-stub}} | {{Chemical-compound-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Endosulfan_Formula_V.3a.svg|Chemical structure of Endosulfan | |||
File:Yellow_toxicity_label.svg|Toxicity warning label | |||
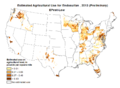
File:Endosulfan_USA_2013.png|Endosulfan usage in the USA, 2013 | |||
File:Endosulfan_use_2002_USGS.png|Endosulfan use in 2002 according to USGS | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:27, 18 February 2025
Endosulfan is a pesticide that belongs to the organochlorine group of chemicals, similar to DDT. It is used in agriculture to control pests on crops such as cotton, rice, and fruit trees. Despite its widespread use, endosulfan is highly toxic and poses significant risks to human health and the environment.
Chemical Properties[edit]
Endosulfan is a colorless to pale yellow solid with a distinct sulfur odor. It is poorly soluble in water but readily soluble in many organic solvents. It is stable under normal storage conditions but can decompose under high heat, producing toxic gases such as sulfur dioxide and hydrogen chloride.
Uses[edit]
Endosulfan has been used as a pesticide since the 1950s. It is effective against a wide range of pests, including aphids, mites, and whiteflies. It is typically applied as a spray to the leaves of crops. However, due to its high toxicity and persistence in the environment, its use is being phased out in many countries.
Health Effects[edit]
Exposure to endosulfan can cause a range of health effects, from mild irritation to severe poisoning. Acute exposure can cause nausea, vomiting, seizures, and even death. Chronic exposure can lead to neurological damage, reproductive health problems, and possibly cancer. Endosulfan can enter the body through the skin, by inhalation, or by ingestion of contaminated food or water.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Endosulfan is highly toxic to aquatic life and birds. It can persist in the environment for long periods, especially in soil and sediments. It can also bioaccumulate in the food chain, posing a risk to wildlife and humans. Efforts are being made to reduce the environmental impact of endosulfan through better management practices and the development of safer alternatives.
Regulation[edit]
The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants, an international environmental treaty, has listed endosulfan for elimination due to its high toxicity and persistence. Many countries, including the European Union and the United States, have banned or severely restricted its use.
See Also[edit]
![]()
This pesticide-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
This article is a Chemical compound-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Chemical structure of Endosulfan
-
Toxicity warning label
-
Endosulfan usage in the USA, 2013
-
Endosulfan use in 2002 according to USGS