Tropane alkaloid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
[[Category:Alkaloids]] | [[Category:Alkaloids]] | ||
[[Category:Tropane alkaloids]] | [[Category:Tropane alkaloids]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Tropane.svg|Tropane structure | |||
File:Tropane_alkaloids_biochemistry.png|Biochemistry of tropane alkaloids | |||
File:CocaineBiosyn2.png|Biosynthesis of cocaine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:04, 18 February 2025
Class of chemical compounds
| Chemical Compound | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider ID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical Formula | |
| Molar Mass | |
| Appearance | |
| Density | |
| Melting Point | |
| Boiling Point | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS Pictograms | [[File:|50px]] |
| GHS Signal Word | |
| GHS Hazard Statements | |
| NFPA 704 | [[File:|50px]] |
| References | |
Tropane alkaloids are a class of alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. These compounds are primarily found in the Solanaceae family, which includes plants such as Atropa belladonna (deadly nightshade), Datura stramonium (jimson weed), and Hyoscyamus niger (henbane).
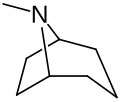
Chemical structure[edit]
The core structure of tropane alkaloids is the tropane ring, a bicyclic structure consisting of a seven-membered ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. This structure is depicted in the image below:

Biosynthesis[edit]
Tropane alkaloids are biosynthesized in plants through a series of enzymatic reactions. The biosynthetic pathway begins with the amino acid ornithine, which undergoes a series of transformations to form the tropane ring. The pathway involves several key enzymes, including ornithine decarboxylase and tropinone reductase.

Notable tropane alkaloids[edit]
Some of the most well-known tropane alkaloids include:
- Atropine - Found in Atropa belladonna, it is used medically to dilate pupils and as an antidote for certain types of poisoning.
- Scopolamine - Found in Datura and Hyoscyamus species, it is used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea.
- Cocaine - Found in the leaves of the Erythroxylum coca plant, it is a powerful stimulant and local anesthetic.
Pharmacology[edit]
Tropane alkaloids exert their effects primarily by interacting with the nervous system. Atropine and scopolamine are known for their anticholinergic properties, meaning they block the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors. Cocaine, on the other hand, acts as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, leading to increased levels of dopamine in the brain and producing its stimulant effects.
Toxicity[edit]
Many tropane alkaloids are highly toxic and can cause severe physiological effects if ingested in large quantities. Symptoms of tropane alkaloid poisoning include dry mouth, dilated pupils, urinary retention, hallucinations, and in severe cases, death.
Cultural and historical significance[edit]
Tropane alkaloids have been used historically in various cultural and medicinal contexts. For example, extracts from plants containing these alkaloids were used in ancient rituals and as poisons. In modern medicine, they continue to be important for their therapeutic properties.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Tropane structure
-
Biochemistry of tropane alkaloids
-
Biosynthesis of cocaine